Control of T cell antigen reactivity via programmed TCR downregulation
- PMID: 26901151
- PMCID: PMC4803589
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.3386
Control of T cell antigen reactivity via programmed TCR downregulation
Abstract
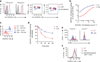
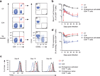
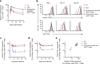
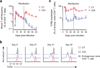
The T cell antigen receptor (TCR) is unique in that its affinity for ligand is unknown before encounter and can vary by orders of magnitude. How the immune system regulates individual T cells that display very different reactivity to antigen remains unclear. Here we found that activated CD4(+) T cells, at the peak of clonal expansion, persistently downregulated their TCR expression in proportion to the strength of the initial antigen recognition. This programmed response increased the threshold for cytokine production and recall proliferation in a clone-specific manner and ultimately excluded clones with the highest antigen reactivity. Thus, programmed downregulation of TCR expression represents a negative feedback mechanism for constraining T cell effector function with a suitable time delay to thereby allow pathogen control while avoiding excess inflammatory damage.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

