Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zerumbone against Mono-Iodoacetate-Induced Arthritis
- PMID: 26901193
- PMCID: PMC4783979
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17020249
Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zerumbone against Mono-Iodoacetate-Induced Arthritis
Abstract
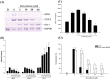
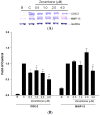
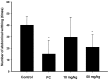
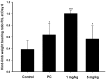
The fresh rhizome of Zingiber zerumbet Smith (Zingiberaceae) is used as a food flavoring and also serves as a folk medicine as an antipyretic and for analgesics in Taiwan. Zerumbone, a monocyclic sesquiterpene was isolated from the rhizome of Z. zerumbet and is the major active compound. In this study, the anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of zerumbone on arthritis were explored using in vitro and in vivo models. Results showed that zerumbone inhibited inducible nitric oxide (NO) synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 expressions, and NO and prostaglandin E₂ (PGE₂) production, but induced heme oxygenase (HO)-1 expression in a dose-dependent manner in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. When zerumbone was co-treated with an HO-1 inhibitor (tin protoporphyrin (SnPP)), the NO inhibitory effects of zerumbone were recovered. The above results suggest that zerumbone inhibited iNOS and COX-2 through induction of the HO-1 pathway. Moreover, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 and COX-2 expressions of interleukin (IL)-1β-stimulated primary rat chondrocytes were inhibited by zerumbone. In an in vivo assay, an acetic acid-induced writhing response in mice was significantly reduced by treatment with zerumbone. Furthermore, zerumbone reduced paw edema and the pain response in a mono-iodoacetate (MIA)-induced rat osteoarthritis model. Therefore, we suggest that zerumbone possesses anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects which indicate zerumbone could be a potential candidate for osteoarthritis treatment.
Keywords: Zingiber zerumbet Smith; anti-inflammatory; arthritis; heme oxygenase-1; metalloproteinase; zerumbone.
Figures


References
-
- Prasannan R., Kalesh K.A., Shanmugam M.K., Nachiyappan A., Ramachandran L., Nguyen A.H., Kumar A.P., Lakshmanan M., Ahn K.S., Sethi G. Key cell signaling pathways modulated by zerumbone: Role in the prevention and treatment of cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012;84:1268–1276. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.07.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chien T.Y., Chen L.G., Lee C.J., Lee F.Y., Wang C.C. Anti-inflammatory constituents of Zingiber zerumbet. Food Chem. 2008;110:584–589. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.02.038. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

