Perspective: Adhesion Mediated Signal Transduction in Bacterial Pathogens
- PMID: 26901228
- PMCID: PMC4810144
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens5010023
Perspective: Adhesion Mediated Signal Transduction in Bacterial Pathogens
Abstract
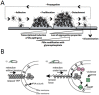
During the infection process, pathogenic bacteria undergo large-scale transcriptional changes to promote virulence and increase intrahost survival. While much of this reprogramming occurs in response to changes in chemical environment, such as nutrient availability and pH, there is increasing evidence that adhesion to host-tissue can also trigger signal transduction pathways resulting in differential gene expression. Determining the molecular mechanisms of adhesion-mediated signaling requires disentangling the contributions of chemical and mechanical stimuli. Here we highlight recent work demonstrating that surface attachment drives a transcriptional response in bacterial pathogens, including uropathogenic Escherichia coli (E. coli), and discuss the complexity of experimental design when dissecting the specific role of adhesion-mediated signaling during infection.
Keywords: adhesion; fimbriae; signal transduction; uropathogenic E. coli; virulence.
Figures


References
-
- Subashchandrabose S., Hazen T.H., Brumbaugh A.R., Himpsl S.D., Smith S.N., Ernst R.D., Rasko D.A., Mobley H.L. Host-specific induction of Escherichia coli fitness genes during human urinary tract infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:18327–18332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1415959112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mavromatis C.H., Bokil N.J., Totsika M., Kakkanat A., Schaale K., Cannistraci C.V., Ryu T., Beatson S.A., Ulett G.C., Schembri M.A., et al. The co-transcriptome of uropathogenic Escherichia coli-infected mouse macrophages reveals new insights into host-pathogen interactions. Cell. Microbiol. 2015;17:730–746. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12397. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

