Mitochondrial DNA copy number variation across human cancers
- PMID: 26901439
- PMCID: PMC4775221
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.10769
Mitochondrial DNA copy number variation across human cancers
Abstract
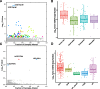
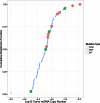
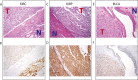
Mutations, deletions, and changes in copy number of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), are observed throughout cancers. Here, we survey mtDNA copy number variation across 22 tumor types profiled by The Cancer Genome Atlas project. We observe a tendency for some cancers, especially of the bladder, breast, and kidney, to be depleted of mtDNA, relative to matched normal tissue. Analysis of genetic context reveals an association between incidence of several somatic alterations, including IDH1 mutations in gliomas, and mtDNA content. In some but not all cancer types, mtDNA content is correlated with the expression of respiratory genes, and anti-correlated to the expression of immune response and cell-cycle genes. In tandem with immunohistochemical evidence, we find that some tumors may compensate for mtDNA depletion to sustain levels of respiratory proteins. Our results highlight the extent of mtDNA copy number variation in tumors and point to related therapeutic opportunities.
Keywords: cancer; computational biology; copy number; human; human biology; medicine; metabolism; mitochondria; mtDNA; sequencing; systems biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures

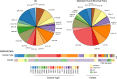
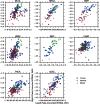
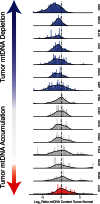
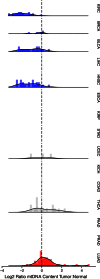





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

