Validation of a Spanish version of the Leicester Cough Questionnaire in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis
- PMID: 26902541
- PMCID: PMC5734594
- DOI: 10.1177/1479972316632005
Validation of a Spanish version of the Leicester Cough Questionnaire in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis
Abstract
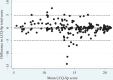
The Leicester Cough Questionnaire (LCQ) has been validated in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis (NCFBC). The present study aimed to create and validate a Spanish version of the LCQ (LCQ-Sp) in NCFBC. The LCQ-Sp was developed following a standardized protocol. For reliability, we assessed internal consistency and the change in score over a 15-day period in stable state. For responsiveness, we assessed the change in scores between visit 1 and the first exacerbation. For validity, we evaluated convergent validity through correlation with the Saint George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) and discriminant validity. Two hundred fifty-nine patients (118 mild bronchiectasis, 90 moderate bronchiectasis and 47 severe bronchiectasis) were included. Internal consistency was high for the total scoring and good for the different domains (Cronbach's α: 0.86-0.91). The test-retest reliability shows an intraclass correlation coefficient of 0.87 for the total score. The mean LCQ-Sp score at visit 1 decreased at the beginning of an exacerbation (15.13 ± 4.06 vs. 12.24 ± 4.64; p < 0.001). The correlation between LCQ-Sp and SGRQ scores was -0.66 (p < 0.01). The differences in the LCQ-Sp total score between the different groups of severity were significant (p < 0.001). The LCQ-Sp discriminates disease severity, is responsive to change when faced with exacerbations and is reliable for use in bronchiectasis.
Keywords: Bronchiectasis; cough; patient-reported outcome; quality of life; questionnaire.
© The Author(s) 2016.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of a Spanish version of the Leicester Cough Questionnaire in cystic fibrosis.Chron Respir Dis. 2021 Jan-Dec;18:14799731211036903. doi: 10.1177/14799731211036903. Chron Respir Dis. 2021. PMID: 34730449 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Leicester Cough Questionnaire in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis.Eur Respir J. 2009 Jul;34(1):125-31. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00160508. Epub 2009 Feb 5. Eur Respir J. 2009. PMID: 19196812
-
Validation of the Mandarin Chinese version of the Leicester Cough Questionnaire in bronchiectasis.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2014 Dec;18(12):1431-7. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.14.0195. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2014. PMID: 25517807
-
Psychometrics of health-related quality of life questionnaires in bronchiectasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Respir J. 2021 Nov 11;58(5):2100025. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00025-2021. Print 2021 Nov. Eur Respir J. 2021. PMID: 33888521 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise training for bronchiectasis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 6;4(4):CD013110. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013110.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33822364 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nebulized hypertonic saline in noncystic fibrosis bronchiectasis: a comprehensive review.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2019 Jan-Dec;13:1753466619866102. doi: 10.1177/1753466619866102. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2019. PMID: 31390940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and functional characteristics, possible causes, and impact of chronic cough in patients with cerebellar ataxia, neuropathy, and bilateral vestibular areflexia syndrome (CANVAS).J Neurol. 2024 Mar;271(3):1204-1212. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-12001-9. Epub 2023 Nov 2. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 37917234 Free PMC article.
-
Physical Deconditioning in Lung Cancer Patients Who Underwent Lung Resection Surgery in Spain: A Prospective Observational Study.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 8;16(16):2790. doi: 10.3390/cancers16162790. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199563 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and Validity of Computerized Adventitious Respiratory Sounds in People with Bronchiectasis.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 19;11(24):7509. doi: 10.3390/jcm11247509. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36556124 Free PMC article.
-
Exacerbations and Changes in Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour in Patients with Bronchiectasis after 1 Year.J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 12;10(6):1190. doi: 10.3390/jcm10061190. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33809173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vendrell M, de Gracia J, Olveira C, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of bronchiectasis. Spanish society of pneumology and thoracic surgery. Arch Bronconeumol 2008; 44: 629–640. - PubMed
-
- Murray MP, Govan JRW, Doherty CJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial of nebulized gentamicin in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011; 183: 491–499. - PubMed
-
- Jones PW, Quirk FH, Baveystock CM, et al. A self-completed measure for chronic airflow limitation: the St George’s respiratory questionnaire. Am Rev Respir Dis 1992; 145: 1321–1327. - PubMed
-
- Wilson CB, Paul WJ, O’leary CJ, et al. Validation of the St. George’s respiratory questionnaire in bronchiectasis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1997; 156: 536–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

