The Structural Basis of Oncogenic Mutations G12, G13 and Q61 in Small GTPase K-Ras4B
- PMID: 26902995
- PMCID: PMC4763299
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21949
The Structural Basis of Oncogenic Mutations G12, G13 and Q61 in Small GTPase K-Ras4B
Abstract
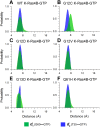
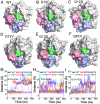
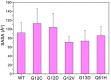
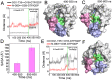
Ras mediates cell proliferation, survival and differentiation. Mutations in K-Ras4B are predominant at residues G12, G13 and Q61. Even though all impair GAP-assisted GTP → GDP hydrolysis, the mutation frequencies of K-Ras4B in human cancers vary. Here we aim to figure out their mechanisms and differential oncogenicity. In total, we performed 6.4 μs molecular dynamics simulations on the wild-type K-Ras4B (K-Ras4B(WT)-GTP/GDP) catalytic domain, the K-Ras4B(WT)-GTP-GAP complex, and the mutants (K-Ras4B(G12C/G12D/G12V)-GTP/GDP, K-Ras4B(G13D)-GTP/GDP, K-Ras4B(Q61H)-GTP/GDP) and their complexes with GAP. In addition, we simulated 'exchanged' nucleotide states. These comprehensive simulations reveal that in solution K-Ras4B(WT)-GTP exists in two, active and inactive, conformations. Oncogenic mutations differentially elicit an inactive-to-active conformational transition in K-Ras4B-GTP; in K-Ras4B(G12C/G12D)-GDP they expose the bound nucleotide which facilitates the GDP-to-GTP exchange. These mechanisms may help elucidate the differential mutational statistics in K-Ras4B-driven cancers. Exchanged nucleotide simulations reveal that the conformational transition is more accessible in the GTP-to-GDP than in the GDP-to-GTP exchange. Importantly, GAP not only donates its R789 arginine finger, but stabilizes the catalytically-competent conformation and pre-organizes catalytic residue Q61; mutations disturb the R789/Q61 organization, impairing GAP-mediated GTP hydrolysis. Together, our simulations help provide a mechanistic explanation of key mutational events in one of the most oncogenic proteins in cancer.
Figures



References
-
- Milburn M. V. et al.. Molecular switch for signal transduction: structural differences between active and inactive forms of protooncogenic ras proteins. Science 247, 939–45 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Cherfils J. & Zeghouf M. Regulation of small GTPases by GEFs, GAPs, and GDIs. Physiol. Rev. 93, 269–309 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Bos J. L., Rehmann H. & Wittinghofer A. Review GEFs and GAPs: Critical elements in the control of small G proteins. Cell 129, 865–877 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Sondermann H. et al.. Structural Analysis of Autoinhibition in the Ras Activator Son of Sevenless. Cell 119, 393–405 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

