Analysis of Subcellular RNA Fractions Revealed a Transcription-Independent Effect of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha on Splicing, Mediated by Spt5
- PMID: 26903558
- PMCID: PMC4836220
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01117-15
Analysis of Subcellular RNA Fractions Revealed a Transcription-Independent Effect of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha on Splicing, Mediated by Spt5
Abstract
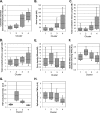
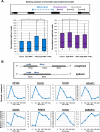
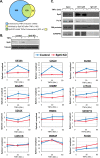
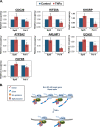
The proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) modulates the expression of many genes, primarily through activation of NF-κB. Here, we examined the global effects of the elongation factor Spt5 on nascent and mature mRNAs of TNF-α-induced cells using chromatin and cytosolic subcellular fractions. We identified several classes of TNF-α-induced genes controlled at the level of transcription, splicing, and chromatin retention. Spt5 was found to facilitate splicing and chromatin release in genes displaying high induction rates. Further analysis revealed striking effects of TNF-α on the splicing of 25% of expressed genes; the vast majority were not transcriptionally induced. Splicing enhancement of noninduced genes by TNF-α was transient and independent of NF-κB. Investigating the underlying basis, we found that Spt5 is required for the splicing facilitation of the noninduced genes. In line with this, Spt5 interacts with Sm core protein splicing factors. Furthermore, following TNF-α treatment, levels of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) but not Spt5 are reduced from the splicing-induced genes, suggesting that these genes become enriched with a Pol II-Spt5 form. Our findings revealed the Pol II-Spt5 complex as a highly competent coordinator of cotranscriptional splicing.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The elongation factor Spt5 facilitates transcription initiation for rapid induction of inflammatory-response genes.Nat Commun. 2016 May 16;7:11547. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11547. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27180651 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Spt5-Pol II by Small-Molecule Inhibitors Uncouples Distinct Activities and Reveals Additional Regulatory Roles.Mol Cell. 2019 Nov 21;76(4):617-631.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.08.024. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31564557
-
DSIF restricts NF-κB signaling by coordinating elongation with mRNA processing of negative feedback genes.Cell Rep. 2012 Oct 25;2(4):722-31. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.08.041. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Cell Rep. 2012. PMID: 23041311
-
Y14 positively regulates TNF-α-induced NF-κB transcriptional activity via interacting RIP1 and TRADD beyond an exon junction complex protein.J Immunol. 2013 Aug 1;191(3):1436-44. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300501. Epub 2013 Jul 1. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23817415
-
Splicing regulation in neurons: tinkering with cell-specific control.Cell. 1998 Mar 20;92(6):709-12. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81399-9. Cell. 1998. PMID: 9529247 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Lowering mutant huntingtin by small molecules relieves Huntington's disease symptoms and progression.EMBO Mol Med. 2024 Mar;16(3):523-546. doi: 10.1038/s44321-023-00020-y. Epub 2024 Feb 19. EMBO Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38374466 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast transcription elongation factor Spt4/5 is a sequence-specific RNA binding protein.Protein Sci. 2016 Sep;25(9):1710-21. doi: 10.1002/pro.2976. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Protein Sci. 2016. PMID: 27376968 Free PMC article.
-
RBM22 regulates RNA polymerase II 5' pausing, elongation rate, and termination by coordinating 7SK-P-TEFb complex and SPT5.Genome Biol. 2024 Apr 19;25(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s13059-024-03242-6. Genome Biol. 2024. PMID: 38641822 Free PMC article.
-
BGL3 lncRNA mediates retention of the BRCA1/BARD1 complex at DNA damage sites.EMBO J. 2020 Jun 17;39(12):e104133. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019104133. Epub 2020 Apr 29. EMBO J. 2020. PMID: 32347575 Free PMC article.
-
Spt5 Plays Vital Roles in the Control of Sense and Antisense Transcription Elongation.Mol Cell. 2017 Apr 6;66(1):77-88.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.023. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28366642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindstrom DL, Squazzo SL, Muster N, Burckin TA, Wachter KC, Emigh CA, McCleery JA, Yates JR III, Hartzog GA. 2003. Dual roles for Spt5 in pre-mRNA processing and transcription elongation revealed by identification of Spt5-associated proteins. Mol Cell Biol 23:1368–1378. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.4.1368-1378.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
