Autoinducer-2 of Streptococcus mitis as a Target Molecule to Inhibit Pathogenic Multi-Species Biofilm Formation In Vitro and in an Endotracheal Intubation Rat Model
- PMID: 26903968
- PMCID: PMC4744849
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00088
Autoinducer-2 of Streptococcus mitis as a Target Molecule to Inhibit Pathogenic Multi-Species Biofilm Formation In Vitro and in an Endotracheal Intubation Rat Model
Abstract
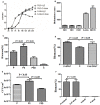
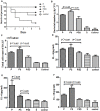
Streptococcus mitis (S. mitis) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) are typically found in the upper respiratory tract of infants. We previously found that P. aeruginosa and S. mitis were two of the most common bacteria in biofilms on newborns' endotracheal tubes (ETTs) and in their sputa and that S. mitis was able to produce autoinducer-2 (AI-2), whereas P. aeruginosa was not. Recently, we also found that exogenous AI-2 and S. mitis could influence the behaviors of P. aeruginosa. We hypothesized that S. mitis contributes to this interspecies interaction and that inhibition of AI-2 could result in inhibition of these effects. To test this hypothesis, we selected PAO1 as a representative model strain of P. aeruginosa and evaluated the effect of S. mitis as well as an AI-2 analog (D-ribose) on mono- and co-culture biofilms in both in vitro and in vivo models. In this context, S. mitis promoted PAO1 biofilm formation and pathogenicity. Dual-species (PAO1 and S. mitis) biofilms exhibited higher expression of quorum sensing genes than single-species (PAO1) biofilms did. Additionally, ETTs covered in dual-species biofilms increased the mortality rate and aggravated lung infection compared with ETTs covered in mono-species biofilms in an endotracheal intubation rat model, all of which was inhibited by D-ribose. Our results demonstrated that S. mitis AI-2 plays an important role in interspecies interactions with PAO1 and may be a target for inhibition of biofilm formation and infection in ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Keywords: AI-2; PAO1; Streptococcus mitis; biofilms; ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of Autoinducer-2 Quorum Sensing Inhibitor on Interspecies Quorum Sensing.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 28;13:791802. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.791802. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35418956 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Streptococcus mitis mixed infection on TLR4-mediated immune response in acute pneumonia mouse model.BMC Microbiol. 2017 Apr 4;17(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12866-017-0999-1. BMC Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28376744 Free PMC article.
-
Does Streptococcus mitis, a neonatal oropharyngeal bacterium, influence the pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa?Microbes Infect. 2015 Oct;17(10):710-6. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Microbes Infect. 2015. PMID: 26277756
-
Autoinducer-2 Facilitates Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Pathogenicity in Vitro and in Vivo.Front Microbiol. 2017 Oct 17;8:1944. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01944. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29089927 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation on endotracheal tubes requires multiple two-component systems.J Med Microbiol. 2020 Jun;69(6):906-919. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001199. Epub 2020 May 21. J Med Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32459613
Cited by
-
Probiotics Streptococcus salivarius 24SMB and Streptococcus oralis 89a interfere with biofilm formation of pathogens of the upper respiratory tract.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Dec 13;18(1):653. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3576-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30545317 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Quorum Sensing Systems on Regulatory T Cells in Catheter-Related Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Infection Rat Models.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:4012912. doi: 10.1155/2016/4012912. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27069314 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Autoinducer-2 Quorum Sensing Inhibitor on Interspecies Quorum Sensing.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 28;13:791802. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.791802. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35418956 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Streptococcus mitis mixed infection on TLR4-mediated immune response in acute pneumonia mouse model.BMC Microbiol. 2017 Apr 4;17(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12866-017-0999-1. BMC Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28376744 Free PMC article.
-
Testing Anti-Biofilm Polymeric Surfaces: Where to Start?Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 3;20(15):3794. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153794. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31382580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baldan R., Cigana C., Testa F., Bianconi I., De Simone M., Pellin D., et al. (2014). Adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis airways influences virulence of Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and murine models of co-infection. PLoS ONE 9:e89614 10.1371/journal.pone.0089614 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belkaid Y., Hoffmann K. F., Mendez S., Kamhawi S., Udey M. C., Wynn T. A., et al. (2001). The role of interleukin (il)-10 in the persistence of leishmania major in the skin after healing and the therapeutic potential of anti-il-10 receptor antibody for sterile cure. J. Exp. Med. 194 1497–1506. 10.1084/jem.194.10.1497 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

