Cryptococcus and Phagocytes: Complex Interactions that Influence Disease Outcome
- PMID: 26903984
- PMCID: PMC4746234
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00105
Cryptococcus and Phagocytes: Complex Interactions that Influence Disease Outcome
Abstract
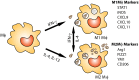
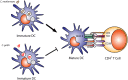
Cryptococcus neoformans and C. gattii are fungal pathogens that cause life-threatening disease. These fungi commonly enter their host via inhalation into the lungs where they encounter resident phagocytes, including macrophages and dendritic cells, whose response has a pronounced impact on the outcome of disease. Cryptococcus has complex interactions with the resident and infiltrating innate immune cells that, ideally, result in destruction of the yeast. These phagocytic cells have pattern recognition receptors that allow recognition of specific cryptococcal cell wall and capsule components. However, Cryptococcus possesses several virulence factors including a polysaccharide capsule, melanin production and secretion of various enzymes that aid in evasion of the immune system or enhance its ability to thrive within the phagocyte. This review focuses on the intricate interactions between the cryptococci and innate phagocytic cells including discussion of manipulation and evasion strategies used by Cryptococcus, anti-cryptococcal responses by the phagocytes and approaches for targeting phagocytes for the development of novel immunotherapeutics.
Keywords: Cryptococcus; Cryptococcus gattii; Cryptococcus neoformans; cryptococcosis; fungal immunity; innate immune response; medical mycology.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

