The Plant Heat Stress Transcription Factors (HSFs): Structure, Regulation, and Function in Response to Abiotic Stresses
- PMID: 26904076
- PMCID: PMC4746267
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00114
The Plant Heat Stress Transcription Factors (HSFs): Structure, Regulation, and Function in Response to Abiotic Stresses
Abstract
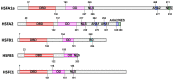
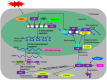
Abiotic stresses such as high temperature, salinity, and drought adversely affect the survival, growth, and reproduction of plants. Plants respond to such unfavorable changes through developmental, physiological, and biochemical ways, and these responses require expression of stress-responsive genes, which are regulated by a network of transcription factors (TFs), including heat stress transcription factors (HSFs). HSFs play a crucial role in plants response to several abiotic stresses by regulating the expression of stress-responsive genes, such as heat shock proteins (Hsps). In this review, we describe the conserved structure of plant HSFs, the identification of HSF gene families from various plant species, their expression profiling under abiotic stress conditions, regulation at different levels and function in abiotic stresses. Despite plant HSFs share highly conserved structure, their remarkable diversification across plants reflects their numerous functions as well as their integration into the complex stress signaling and response networks, which can be employed in crop improvement strategies via biotechnological intervention.
Keywords: abiotic stress; heat shock proteins; heat stress; plant; transcription factors; transcriptional regulation.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

