Involvement of Mu Opioid Receptor Signaling in the Protective Effect of Opioid against 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cells Apoptosis
- PMID: 26904174
- PMCID: PMC4656990
Involvement of Mu Opioid Receptor Signaling in the Protective Effect of Opioid against 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cells Apoptosis
Abstract
Introduction: The neuroprotective role of opioid morphine against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced cell death has been demonstrated. However, the exact mechanism(s) underlying such neuroprotection, especially the role of subtype receptors, has not yet been fully clarified.
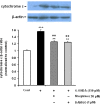
Methods: Here, we investigated the effects of different opioid agonists on 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line as an in vitro model of Parkinson's disease. Cell damage was induced by 150 μM 6-OHDA and the cells viability was examined by MTT assay. Intracellular calcium, reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial membrane potential were assessed by fluorescence spectrophotometry method. Immunoblot technique was used to evaluate cytochrome-c and activated caspase-3 as biochemical markers of apoptosis induction.
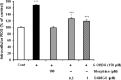
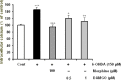
Results: The data showed that 6-OHDA caused significant cell damage, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species and calcium levels as well as activated caspase-3 and cytochrome-c release. Incubation of SH-SY5Y cells with μ-opioid agonists, morphine and DAMGO, but not with δ-opioid agonist, DADLE, elicited protective effect and reduced biochemical markers of cell damage and death.
Discussion: The results suggest that μ-opioid receptors signaling participate in the opioid neuroprotective effects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity.
Keywords: 6-hydroxydopamine; Apoptosis; DAMGO; Morphine; SH-SY5Y cells; μ-opioid receptors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Morphine protects SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced cell damage: involvement of anti-oxidant, calcium blocking, and anti-apoptotic properties.Rejuvenation Res. 2014 Jun;17(3):255-63. doi: 10.1089/rej.2013.1473. Rejuvenation Res. 2014. PMID: 24341565
-
Phytohormone Abscisic Acid Protects Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells Against 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Neurotoxicity Through Its Antioxidant and Antiapoptotic Properties.Rejuvenation Res. 2019 Apr;22(2):99-108. doi: 10.1089/rej.2018.2062. Epub 2018 Oct 6. Rejuvenation Res. 2019. PMID: 30091676
-
Protective Effect of Neuropeptide Apelin-13 on 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Dopaminergic Cells: Involvement of Its Antioxidant and Antiapoptotic Properties.Rejuvenation Res. 2018 Apr;21(2):162-167. doi: 10.1089/rej.2017.1951. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Rejuvenation Res. 2018. PMID: 28782414
-
Protective effect of orexin-A on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y human dopaminergic neuroblastoma cells.Neurochem Int. 2013 Dec;63(8):719-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.09.022. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Neurochem Int. 2013. PMID: 24135219
-
Induction of cross-tolerance between protective effect of morphine and nicotine in 6-hydroxydopamine-induce neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y human dopaminergic neuroblastoma cells.Int J Neurosci. 2019 Feb;129(2):129-138. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2018.1494169. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Int J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 29947270
Cited by
-
Reduction in SH-SY5Y Cell Stress Induced by Corticosterone and Attenuation of the Inflammatory Response in RAW 264.7 Cells Using Endomorphin Analogs.Biomedicines. 2025 Jul 20;13(7):1774. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071774. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722844 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-Brain Barrier Transporters: Opportunities for Therapeutic Development in Ischemic Stroke.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 8;23(3):1898. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031898. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphine pretreatment protects against cerebral ischemic injury via a cPKCγ-mediated anti-apoptosis pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Sep;22(3):1016. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10448. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34373702 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Delivery of a Potent Opioid Receptor Agonist, Biphalin during Ischemic Stroke: Role of Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide (OATP).Pharmaceutics. 2019 Sep 10;11(9):467. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11090467. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31509975 Free PMC article.
-
Transport Mechanisms at the Blood-Brain Barrier and in Cellular Compartments of the Neurovascular Unit: Focus on CNS Delivery of Small Molecule Drugs.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jul 20;14(7):1501. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071501. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35890396 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chakass D., Philippe D., Erdual E., Dharancy S., Malapel M., Dubuquoy C., Thuru X., Gay J., Gaveriaux-Ruff C., Dubus P., Mathurin P., Kieffer B. L., Desreumaux P., Chamaillard M. (2007). Micro-Opioid receptor activation prevents acute hepatic inflammation and cell death. Gut, 56(7), 974– 81. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
