Medical management of neurogenic bladder with oral therapy
- PMID: 26904412
- PMCID: PMC4739981
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2015.12.07
Medical management of neurogenic bladder with oral therapy
Abstract
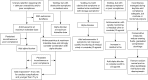
This is a review of the most current literature on medical management of the neurogenic bladder (NGB) to treat detrusor overactivity (DO), improve bladder compliance and treat urinary incontinence. The use of antimuscarinics, alpha blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, desmopressin and mirabegron will be discussed along with combination therapy to improve efficacy. These medical therapies will be the focus of this review with surgical therapy and botulinum toxin injections being the subject of other articles in this series.
Keywords: Neurogenic bladder (NGB); adrenergic alpha blockers; antimuscarinics; desmopressin; imipramine; mirabegron.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cameron AP, Wallner LP, Tate DG, et al. Bladder management after spinal cord injury in the United States 1972 to 2005. J Urol 2010;184:213-7. - PubMed
-
- Nortvedt MW, Riise T, Frugård J, et al. Prevalence of bladder, bowel and sexual problems among multiple sclerosis patients two to five years after diagnosis. Mult Scler 2007;13:106-12. - PubMed
-
- Nicholas RS, Friede T, Hollis S, et al. Anticholinergics for urinary symptoms in multiple sclerosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009;(1):CD004193. - PubMed
-
- Torre M, Guida E, Bisio G, et al. Risk factors for renal function impairment in a series of 502 patients born with spinal dysraphisms. J Pediatr Urol 2011;7:39-43. - PubMed
-
- Gerridzen RG, Thijssen AM, Dehoux E. Risk factors for upper tract deterioration in chronic spinal cord injury patients. J Urol 1992;147:416-8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources