Assessment of serum prolactin levels in acute myocardial infarction: The role of pharmacotherapy
- PMID: 26904472
- PMCID: PMC4743388
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-8210.172240
Assessment of serum prolactin levels in acute myocardial infarction: The role of pharmacotherapy
Abstract
Background: Hyperprolactinemia may reflect neuroendocrine stress reaction against acute coronary syndromes.
Aim: The aim of the present study was evaluation of the serum prolactin level in the acute myocardial infarction (MI) regarding the current pharmacotherapy in management of MI.
Setting and design: Cross-sectional clinical based study.
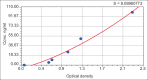
Subjects and methods: This cross-sectional clinical study involved all patients with acute MI in a coronary care unit, a total number of 44 patients (45% males and 55% females) with age ranged from 40 to 75 years. A full history for modifiable risk factors and current therapy with aspirin, clopidogrel and or metformin, all patients are nonsmokers. The anthropometric measurements; for estimations of body mass index (kg/m(2)), electrocardiography was obtained. Fasting blood samples were taken in the morning from all patients and the sera used for estimations of routine investigation and determination of ischemic cardiac biomarkers like cardiac troponin I (cTnI) and serum prolactin level.
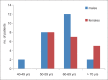
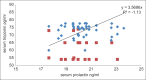
Results: This study shows a significant increase in the serum prolactin in acute MI as compared with the control. In acute MI serum cTnI elevation was correlated with serum prolactin increments. In metformin-treated group, there was a lowest prolactin serum level.
Conclusions: Serum prolactin level increased in acute MI, and positively correlated with cardiac troponin level and reflects underlying cardiovascular complications.
Keywords: Acute myocardial infarction; metformin; prolactin.
Figures
References
-
- Kokot I, Pawlik-Sobecka L, Placzkowska S, Piwowar A. Prolactin as an immunomodulatory factor in psoriatic arthritis. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online) 2013;67:1265–72. - PubMed
-
- Southgate TD, Windeatt S, Smith-Arica J, Gerdes CA, Perone MJ, Morris I, et al. Transcriptional targeting to anterior pituitary lactotrophic cells using recombinant adenovirus vectors in vitro and in vivo in normal and estrogen/sulpiride-induced hyperplastic anterior pituitaries. Endocrinology. 2000;141:3493–505. - PubMed
-
- Jin J, Hashizume T. Effects of hypothalamic dopamine on growth hormone-releasing hormone-induced growth hormone secretion and thyrotropin-releasing hormone-induced prolactin secretion in goats. Anim Sci J. 2015;86:634–40. - PubMed
-
- Bu G, Liang X, Li J, Wang Y. Extra-pituitary prolactin (PRL) and prolactin-like protein (PRL-L) in chickens and Zebrafish. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2015;220:143–53. - PubMed
-
- Medic-Stojanoska M, Icin T, Pletikosic I, Bajkin I, Novakovic-Paro J, Stokic E, et al. Risk factors for accelerated atherosclerosis in young women with hyperprolactinemia. Med Hypotheses. 2015;84:321–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials