H-NS Nucleoid Protein Controls Virulence Features of Klebsiella pneumoniae by Regulating the Expression of Type 3 Pili and the Capsule Polysaccharide
- PMID: 26904512
- PMCID: PMC4746245
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00013
H-NS Nucleoid Protein Controls Virulence Features of Klebsiella pneumoniae by Regulating the Expression of Type 3 Pili and the Capsule Polysaccharide
Abstract
Klebsiella pneumoniae is an opportunistic pathogen causing nosocomial infections. Main virulence determinants of K. pneumoniae are pili, capsular polysaccharide, lipopolysaccharide, and siderophores. The histone-like nucleoid-structuring protein (H-NS) is a pleiotropic regulator found in several gram-negative pathogens. It has functions both as an architectural component of the nucleoid and as a global regulator of gene expression. We generated a Δhns mutant and evaluated the role of the H-NS nucleoid protein on the virulence features of K. pneumoniae. A Δhns mutant down-regulated the mrkA pilin gene and biofilm formation was affected. In contrast, capsule expression was derepressed in the absence of H-NS conferring a hypermucoviscous phenotype. Moreover, H-NS deficiency affected the K. pneumoniae adherence to epithelial cells such as A549 and HeLa cells. In infection experiments using RAW264.7 and THP-1 differentiated macrophages, the Δhns mutant was less phagocytized than the wild-type strain. This phenotype was likely due to the low adherence to these phagocytic cells. Taken together, our data indicate that H-NS nucleoid protein is a crucial regulator of both T3P and CPS of K. pneumoniae.
Keywords: H-NS; K. pneumoniae; T3P; adherence; capsule; phagocytosis; virulence.
Figures

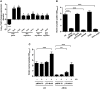
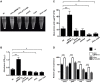
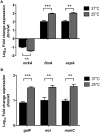
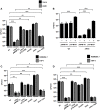
References
-
- Ares M. Á., Alcántar-Curiel M. D., Jiménez-Galicia C., Rios-Sarabia N., Pacheco S., De la Cruz M. Á. (2013). Antibiotic resistance of gram-negative bacilli isolated from pediatric patients with nosocomial bloodstream infections in a Mexican tertiary care hospital. Chemotherapy 59, 361–368. 10.1159/000362085 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

