Viral vectors for therapy of neurologic diseases
- PMID: 26905292
- PMCID: PMC5929167
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.02.013
Viral vectors for therapy of neurologic diseases
Abstract
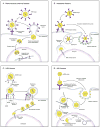
Neurological disorders - disorders of the brain, spine and associated nerves - are a leading contributor to global disease burden with a shockingly large associated economic cost. Various treatment approaches - pharmaceutical medication, device-based therapy, physiotherapy, surgical intervention, among others - have been explored to alleviate the resulting extent of human suffering. In recent years, gene therapy using viral vectors - encoding a therapeutic gene or inhibitory RNA into a "gutted" viral capsid and supplying it to the nervous system - has emerged as a clinically viable option for therapy of brain disorders. In this Review, we provide an overview of the current state and advances in the field of viral vector-mediated gene therapy for neurological disorders. Vector tools and delivery methods have evolved considerably over recent years, with the goal of providing greater and safer genetic access to the central nervous system. Better etiological understanding of brain disorders has concurrently led to identification of improved therapeutic targets. We focus on the vector technology, as well as preclinical and clinical progress made thus far for brain cancer and various neurodegenerative and neurometabolic disorders, and point out the challenges and limitations that accompany this new medical modality. Finally, we explore the directions that neurological gene therapy is likely to evolve towards in the future. This article is part of the Special Issue entitled "Beyond small molecules for neurological disorders".
Keywords: Brain tumors; Gene therapy; Lysosomal storage diseases; Metabolic diseases; Neurodegeneration; Viral vectors.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmed SS, Li H, Cao C, Sikoglu EM, Denninger AR, Su Q, Eaton S, Liso Navarro AA, Xie J, Szucs S, Zhang H, Moore C, Kirschner DA, Seyfried TN, Flotte TR, Matalon R, Gao G. A single intravenous rAAV injection as late as P20 achieves efficacious and sustained CNS gene therapy in Canavan mice. Mol Ther. 2013;21(12):2136–2147. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/mt.2013.138. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aiuti A, Biasco L, Scaramuzza S, Ferrua F, Cicalese MP, Baricordi C, Dionisio F, Calabria A, Giannelli S, Castiello MC, Bosticardo M, Evangelio C, Assanelli A, Casiraghi M, Di Nunzio S, Callegaro L, Benati C, Rizzardi P, Pellin D, Di Serio C, Schmidt M, Von Kalle C, Gardner J, Mehta N, Neduva V, Dow DJ, Galy A, Miniero R, Finocchi A, Metin A, Banerjee PP, Orange JS, Galimberti S, Valsecchi MG, Biffi A, Montini E, Villa A, Ciceri F, Roncarolo MG, Naldini L. Lentiviral hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy in patients with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Science. 2013;341(6148):1233151. http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1233151. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akli S, Caillaud C, Vigne E, Stratford-Perricaudet LD, Poenaru L, Perricaudet M, Kahn A, Peschanski MR. Transfer of a foreign gene into the brain using adenovirus vectors. Nat Genet. 1993;3(3):224–228. - PubMed
-
- Altman-Hamamdzic S, Groseclose C, Ma JX, Hamamdzic D, Vrindavanam NS, Middaugh LD, Parratto NP, Sallee FR. Expression of beta-galactosidase in mouse brain: utilization of a novel nonreplicative Sindbis virus vector as a neuronal gene delivery system. Gene Ther. 1997;4(8):815–822. - PubMed
-
- Anguela XM, Sharma R, Doyon Y, Miller JC, Li H, Haurigot V, Rohde ME, Wong SY, Davidson RJ, Zhou S, Gregory PD, Holmes MC, High KA. Robust ZFN-mediated genome editing in adult hemophilic mice. Blood. 2013;122(19):3283–3287. http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-04-497354. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

