Carbon Monoxide Gas Is Not Inert, but Global, in Its Consequences for Bacterial Gene Expression, Iron Acquisition, and Antibiotic Resistance
- PMID: 26907100
- PMCID: PMC4921903
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2015.6501
Carbon Monoxide Gas Is Not Inert, but Global, in Its Consequences for Bacterial Gene Expression, Iron Acquisition, and Antibiotic Resistance
Abstract
Aims: Carbon monoxide is a respiratory poison and gaseous signaling molecule. Although CO-releasing molecules (CORMs) deliver CO with temporal and spatial specificity in mammals, and are proven antimicrobial agents, we do not understand the modes of CO toxicity. Our aim was to explore the impact of CO gas per se, without intervention of CORMs, on bacterial physiology and gene expression.
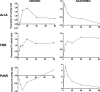
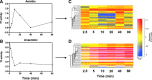
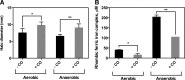
Results: We used tightly controlled chemostat conditions and integrated transcriptomic datasets with statistical modeling to reveal the global effects of CO. CO is known to inhibit bacterial respiration, and we found expression of genes encoding energy-transducing pathways to be significantly affected via the global regulators, Fnr, Arc, and PdhR. Aerobically, ArcA-the response regulator-is transiently phosphorylated and pyruvate accumulates, mimicking anaerobiosis. Genes implicated in iron acquisition, and the metabolism of sulfur amino acids and arginine, are all perturbed. The global iron-related changes, confirmed by modulation of activity of the transcription factor Fur, may underlie enhanced siderophore excretion, diminished intracellular iron pools, and the sensitivity of CO-challenged bacteria to metal chelators. Although CO gas (unlike H2S and NO) offers little protection from antibiotics, a ruthenium CORM is a potent adjuvant of antibiotic activity.
Innovation: This is the first detailed exploration of global bacterial responses to CO, revealing unexpected targets with implications for employing CORMs therapeutically.
Conclusion: This work reveals the complexity of bacterial responses to CO and provides a basis for understanding the impacts of CO from CORMs, heme oxygenase activity, or environmental sources. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 24, 1013-1028.
Figures





References
-
- Adrait A, Jacquamet L, LePape L, dePeredo AG, Aberdam D, Hazemann JL, Latour JM, and Michaud-Soret I. Spectroscopic and saturation magnetization properties of the manganese- and cobalt-substituted Fur (Ferric uptake regulation) protein from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 38: 6248–6260, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Alvarez AF. and Georgellis D. In vitro and in vivo analysis of the ArcB/A redox signaling pathway. Methods Enzymol 471: 205–228, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Asif HM, Rolfe MD, Green J, Lawrence ND, Rattray M, and Sanguinetti G. TFInfer: a tool for probabilistic inference of transcription factor activities. Bioinformatics 26: 2635–2636, 2010 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

