The Protective Role of the TOPK/PBK Pathway in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion and H₂O₂-Induced Injury in H9C2 Cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 26907268
- PMCID: PMC4813131
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17030267
The Protective Role of the TOPK/PBK Pathway in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion and H₂O₂-Induced Injury in H9C2 Cardiomyocytes
Abstract
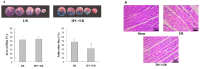
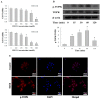
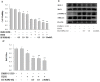
T-LAK-cell-originated protein kinase (TOPK) is a PDZ-binding kinase (PBK) that was recently identified as a novel member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family. It has been shown to play an important role in many cellular functions. However, its role in cardiac function remains unclear. Thus, we have herein explored the biological function of TOPK in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) and oxidative stress injury in H9C2 cardiomyocytes. I/R and ischemic preconditioning (IPC) were induced in rats by 3-hour reperfusion after 30-min occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery and by 3 cycles of 5-min I/R. Hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) was used to induce oxidative stress in H9C2 cardiomyocytes. TOPK expression was analyzed by western blotting, RT-PCR, immunohistochemical staining, and immunofluorescence imaging studies. The effects of TOPK gene overexpression and its inhibition via its inhibitor HI-TOPK-032 on cell viability and Bcl-2, Bax, ERK1/2, and p-ERK1/2 protein expression were analyzed by MTS assay and western blotting, respectively. The results showed that IPC alleviated myocardial I/R injury and induced TOPK activation. Furthermore, H₂O₂ induced TOPK phosphorylation in a time-dependent manner. Interestingly, TOPK inhibition aggravated the H₂O₂-induced oxidative stress injury in myocardiocytes, whereas overexpression relieved it. In addition, the ERK pathway was positively regulated by TOPK signaling. In conclusion, our results indicate that TOPK might mediate a novel survival signal in myocardial I/R, and that its effect on anti-oxidative stress involves the ERK signaling pathway.
Keywords: TOPK/PBK; ischemia/reperfusion; ischemic preconditioning; oxidative stress.
Figures




Similar articles
-
PBK/TOPK: A Therapeutic Target Worthy of Attention.Cells. 2021 Feb 11;10(2):371. doi: 10.3390/cells10020371. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33670114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of T-LAK-cell-originated protein kinase-mediated antioxidation protects against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.FEBS J. 2014 Oct;281(19):4411-20. doi: 10.1111/febs.12948. Epub 2014 Aug 15. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 25065601
-
Ischemic postconditioning relieves cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury through activating T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase/protein kinase B pathway in rats.Stroke. 2014 Aug;45(8):2417-24. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.006135. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Stroke. 2014. PMID: 25013016
-
Cardioprotective effect of Danshensu against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and inhibits apoptosis of H9c2 cardiomyocytes via Akt and ERK1/2 phosphorylation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Jan 15;699(1-3):219-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.11.005. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23200898
-
PBK/TOPK overexpression and survival in solid tumors: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Mar;98(10):e14766. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014766. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30855480 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Machine learning approach identifies inflammatory gene signature for predicting survival outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 5;14(1):30328. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81395-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39638834 Free PMC article.
-
T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase (TOPK): an emerging target for cancer-specific therapeutics.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Oct 24;9(11):1089. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1131-7. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30356039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation to Prevent Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Mar 5;13:28. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00028. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32194375 Free PMC article.
-
PBK/TOPK: A Therapeutic Target Worthy of Attention.Cells. 2021 Feb 11;10(2):371. doi: 10.3390/cells10020371. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33670114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Didymin, a natural flavonoid, relieves the progression of myocardial infarction via inhibiting the NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):2319-2327. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2148170. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 36416076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Otani H., Tanaka H., Inoue T., Umemoto M., Omoto K., Tanaka K., Sato T., Osako T., Masuda A., Nonoyama A., et al. In vitro study on contribution of oxidative metabolism of isolated rabbit heart mitochondria to myocardial reperfusion injury. Circ. Res. 1984;55:168–175. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.55.2.168. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

