Heavy Metals in Surface Soils in the Upper Reaches of the Heihe River, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China
- PMID: 26907322
- PMCID: PMC4808910
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph13030247
Heavy Metals in Surface Soils in the Upper Reaches of the Heihe River, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China
Abstract
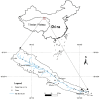
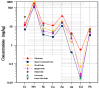
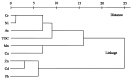
The upper reaches of the Heihe River have been regarded as a hotspot for phytoecology, climate change, water resources and hydrology studies. Due to the cold-arid climate, high elevation, remote location and poor traffic conditions, few studies focused on heavy metal contamination of soils have been conducted or reported in this region. In the present study, an investigation was performed to provide information regarding the concentration levels, sources, spatial distributions, and environmental risks of heavy metals in this area for the first time. Fifty-six surface soil samples collected from the study area were analyzed for Cr, Mn, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd and Pb concentrations, as well as TOC levels. Basic statistics, concentration comparisons, correlation coefficient analysis and multivariate analyses coupled with spatial distributions were utilized to delineate the features and the sources of different heavy metals. Risk assessments, including geoaccumulation index, enrichment factor and potential ecological risk index, were also performed. The results indicate that the concentrations of heavy metals have been increasing since the 1990 s. The mean values of each metal are all above the average background values in the Qinghai Province, Tibet, China and the world, except for that of Cr. Of special note is the concentration of Cd, which is extremely elevated compared with all background values. The distinguished ore-forming conditions and well-preserved, widely distributed limestones likely contribute to the high Cd concentration. Heavy metals in surface soils in the study area are primarily inherited from parent materials. Nonetheless, anthropogenic activities may have accelerated the process of weathering. Cd presents a high background concentration level and poses a severe environmental risk throughout the whole region. Soils in Yinda, Reshui daban, Kekeli and Zamasheng in particular pose threats to the health of the local population, as well as that of livestock and wildlife.
Keywords: Heihe River; Tibetan Plateau; heavy metals; multivariate statistics; risk assessment; soil.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of traffic-related metals and the effects of different environments on their enrichment in roadside soils along the Qinghai-Tibet highway.Sci Total Environ. 2015 Jul 15;521-522:160-72. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.054. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Sci Total Environ. 2015. PMID: 25835375
-
Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2015 Oct;120:377-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.06.019. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2015. PMID: 26114257
-
[Heavy metal pollution characteristics and ecological risk analysis for soil in Phyllostachys praecox stands of Lin'an].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2015 Jun;26(6):1883-91. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26572046 Chinese.
-
Research progress on environmental behavior of arsenic in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau soil.J Environ Sci (China). 2025 Jul;153:237-250. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2024.08.021. Epub 2024 Aug 28. J Environ Sci (China). 2025. PMID: 39855796 Review.
-
Cadmium (Cd) accumulation in traditional Chinese medicine materials (TCMMs): A critical review.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022 Sep 1;242:113904. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113904. Epub 2022 Jul 23. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022. PMID: 35882109 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Study of Hydrochemical Classification Based on Different Hierarchical Cluster Analysis Methods.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Dec 18;17(24):9515. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17249515. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33353090 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Mining and Vegetation Restoration on Soil Properties in the Eastern Margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jun 16;17(12):4288. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17124288. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32560083 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Sources, Pollution, and Ecological Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Surface Soils on the North-Eastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau.Toxics. 2022 Jul 3;10(7):368. doi: 10.3390/toxics10070368. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 35878273 Free PMC article.
-
Shallow Groundwater Quality and Its Controlling Factors in the Su-Xi-Chang Region, Eastern China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Feb 16;17(4):1267. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17041267. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32079130 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Mining Activities on the Release of Heavy Metals (HMs) in a Typical Mountain Headwater Region, the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Sep 12;15(9):1987. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15091987. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30213099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chakraborty P., Babu P.V.R., Acharyya T., Bandyopadhyay D. Stress and toxicity of biologically important transition metals (co, ni, cu and zn) on phytoplankton in a tropical freshwater system: An Investigation with Pigment Analysis by Hplc. Chemosphere. 2010;80:548–553. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.04.039. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Islam M.S., Ahmed M.K., Habibullahalmamun M., Hoque M.F. Preliminary assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from a river in bangladesh. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015;73:1837–1848. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3538-5. - DOI
-
- Meza-Montenegro M.M., Gandolfi A.J., Klimecki W.T., Aguilar-Apodaca M.G., Río-Salas R.D., O-Villanueva M.D.L., Gómez-Alvarez A., Mendivil-Quijada H., Valencia M. Metals in residential soils and cumulative risk assessment in yaqui and mayo agricultural valleys, northern mexico. Sci. Environ. 2012;433:472–481. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.06.083. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

