Abnormal labyrinthine zone in the Hectd1-null placenta
- PMID: 26907377
- PMCID: PMC4768308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2015.12.002
Abnormal labyrinthine zone in the Hectd1-null placenta
Abstract
Introduction: The labyrinthine zone of the placenta is where exchange of nutrients and waste occurs between maternal and fetal circulations. Proper development of the placental labyrinth is essential for successful growth of the developing fetus and abnormalities in placental development are associated with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), preeclampsia and fetal demise. Our previous studies demonstrate that Hectd1 is essential for development of the junctional and labyrinthine zones of the placenta. Here we further characterize labyrinthine zone defects in the Hectd1 mutant placenta.
Methods: The structure of the mutant placenta was compared to wildtype littermates using histological methods. The expression of cell type specific markers was examined by immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization.
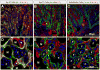
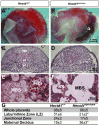
Results: Hectd1 is expressed in the labyrinthine zone throughout development and the protein is enriched in syncytiotrophoblast layer type I cells (SynT-I) and Sinusoidal Trophoblast Giant cells (S-TGCs) in the mature placenta. Mutation of Hectd1 results in pale placentas with frequent hemorrhages along with gross abnormalities in the structure of the labyrinthine zone including a smaller overall volume and a poorly elaborated fetal vasculature that contain fewer fetal blood cells. Examination of molecular markers of labyrinthine trophoblast cell types reveals increased Dlx3 positive cells and Syna positive SynT-I cells, along with decreased Hand1 and Ctsq positive sinusoidal trophoblast giant cells (S-TGCs).
Discussion: Together these defects indicate that Hectd1 is required for development of the labyrinthine zonethe mouse placenta.
Keywords: HECT E3 ligase; Labyrinthine layer; Placenta.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Cross JC, Nakano H, Natale DR, Simmons DG, Watson ED. Branching morphogenesis during development of placental villi. Differentiation; research in biological diversity. 2006;74(7):393–401. - PubMed
-
- Nagy A. Manipulating the mouse embryo : a laboratory manual 2003. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; p. x.p. 764.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

