Hypoglycemia Prevention and User Acceptance of an Insulin Pump System with Predictive Low Glucose Management
- PMID: 26907513
- PMCID: PMC4870649
- DOI: 10.1089/dia.2015.0324
Hypoglycemia Prevention and User Acceptance of an Insulin Pump System with Predictive Low Glucose Management
Abstract
Background: The MiniMed 640G sensor-augmented insulin pump system (Medtronic, Inc., Northridge, CA) can automatically suspend insulin delivery in advance of predicted hypoglycemia and restart it upon recovery. The aims of this analysis were to determine the rate at which predicted hypoglycemia was avoided with this strategy, as well as to assess user acceptance of the system and its insulin management features.
Subjects and methods: Forty subjects with type 1 diabetes used the system for 4 weeks. We retrospectively evaluated performance of the system, using downloaded pump and sensor data, and evaluated user acceptance via questionnaires.
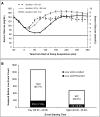
Results: There were 2,322 suspend before low events (2.1 per subject-day). The mean (± SD) duration of pump suspension events was 56.4 ± 9.6 min, and the mean subsequent sensor glucose (SG) nadir was 71.8 ± 5.2 mg/dL. SG values following 1,930 (83.1%) of the predictive suspensions did not reach the preset low limit. Nadir SG values of ≤50 and ≤60 mg/dL were seen in 207 (8.9%) and 356 (15.3%) of the predictive suspensions, respectively. Blood glucose (BG) and SG values before and during the study were comparable (P > 0.05). The mean absolute relative difference between paired SG and BG values was 10.9 ± 13.8%. Subjects felt confident using the system, agreed that it helped protect them from hypoglycemia, and wished to continue using it.
Conclusions: Automatic insulin pump suspension as implemented in the MiniMed 640G system can help patients avoid hypoglycemia, without significantly increasing hyperglycemia.
Figures
Comment in
-
Safety of a Hybrid Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery System in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes.JAMA. 2016 Oct 4;316(13):1407-1408. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.11708. JAMA. 2016. PMID: 27629148 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bergenstal RM, Klonoff DC, Garg SK, Bode BW, Meredith M, Slover RH, Ahmann AJ, Welsh JB, Lee SW, Kaufman FR; ASPIRE In-Home Study Group: Threshold-based insulin-pump interruption for reduction of hypoglycemia. N Engl J Med 2013;369:224–232 - PubMed
-
- Ly TT, Nicholas JA, Retterath A, Lim EM, Davis EA, Jones TW: Effect of sensor-augmented insulin pump therapy and automated insulin suspension vs standard insulin pump therapy on hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013;310:1240–1247 - PubMed
-
- Danne T, Tsioli C, Kordonouri O, Blaesig S, Remus K, Roy A, Keenan B, Lee SW, Kaufman FR: The PILGRIM study: in silico modeling of a predictive low glucose management system and feasibility in youth with type 1 diabetes during exercise. Diabetes Technol Ther 2014;16:338–347 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
