A calpain-2 selective inhibitor enhances learning & memory by prolonging ERK activation
- PMID: 26907807
- PMCID: PMC4873344
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.02.022
A calpain-2 selective inhibitor enhances learning & memory by prolonging ERK activation
Abstract
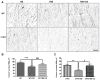
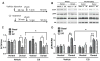
While calpain-1 activation is required for LTP induction by theta burst stimulation (TBS), calpain-2 activation limits its magnitude during the consolidation period. A selective calpain-2 inhibitor applied either before or shortly after TBS enhanced the degree of potentiation. In the present study, we tested whether the selective calpain-2 inhibitor, Z-Leu-Abu-CONH-CH2-C6H3 (3, 5-(OMe)2 (C2I), could enhance learning and memory in wild-type (WT) and calpain-1 knock-out (C1KO) mice. We first showed that C2I could reestablish TBS-LTP in hippocampal slices from C1KO mice, and this effect was blocked by PD98059, an inhibitor of ERK. TBS resulted in PTEN degradation in hippocampal slices from both WT and C1KO mice, and C2I treatment blocked this effect in both mouse genotypes. Systemic injection of C2I 30 min before training in the fear-conditioning paradigm resulted in a biphasic dose-response curve, with low doses enhancing and high doses inhibiting freezing behavior. The difference between the doses needed to enhance and inhibit learning matches the difference in concentrations producing inhibition of calpain-2 and calpain-1. A low dose of C2I also restored normal learning in a novel object recognition task in C1KO mice. Levels of SCOP, a ERK phosphatase known to be cleaved by calpain-1, were decreased in dorsal hippocampus early but not late following training in WT mice; C2I treatment did not affect the early decrease in SCOP levels but prevented its recovery at the later time-point and prolonged ERK activation. The results indicate that calpain-2 activation limits the extent of learning, an effect possibly due to temporal limitation of ERK activation, as a result of SCOP synthesis induced by calpain-2-mediated PTEN degradation.
Keywords: Calpain-1; Calpain-2; ERK; Hippocampus; Learning; SCOP.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
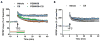
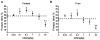
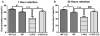
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

