β-aminoisobutyric acid attenuates hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress and glucose/lipid metabolic disturbance in mice with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 26907958
- PMCID: PMC4764829
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21924
β-aminoisobutyric acid attenuates hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress and glucose/lipid metabolic disturbance in mice with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
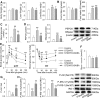
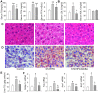
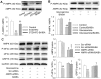
β-aminoisobutyric acid (BAIBA) is a nature thymine catabolite, and contributes to exercise-induced protection from metabolic diseases. Here we show the therapeutical effects of BAIBA on hepatic endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and glucose/lipid metabolic disturbance in diabetes. Type 2 diabetes was induced by combined streptozotocin (STZ) and high-fat diet (HFD) in mice. Oral administration of BAIBA for 4 weeks reduced blood glucose and lipids levels, hepatic key enzymes of gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis expressions, attenuated hepatic insulin resistance and lipid accumulation, and improved insulin signaling in type 2 diabetic mice. BAIBA reduced hepatic ER stress and apoptosis in type 2 diabetic mice. Furthermore, BAIBA alleviated ER stress in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells with glucosamine-induced insulin resistance. Hepatic AMPK phosphorylation was reduced in STZ/HFD mice and glucosamine-treated HepG2 cells, which were restored by BAIBA treatment. The suppressive effects of BAIBA on glucosamine-induced ER stress were reversed by knockdown of AMPK with siRNA. In addition, BAIBA prevented thapsigargin- or tunicamycin-induced ER stress, and tunicamycin-induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells. These results indicate that BAIBA attenuates hepatic ER stress, apoptosis and glucose/lipid metabolic disturbance in mice with type 2 diabetes. AMPK signaling is involved to the role of BAIBA in attenuating ER stress.
Figures



Similar articles
-
BAIBA attenuates insulin resistance and inflammation induced by palmitate or a high fat diet via an AMPK-PPARδ-dependent pathway in mice.Diabetologia. 2015 Sep;58(9):2096-105. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3663-z. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Diabetologia. 2015. PMID: 26105792
-
β-aminoisobutyric acid attenuates LPS-induced inflammation and insulin resistance in adipocytes through AMPK-mediated pathway.J Biomed Sci. 2018 Mar 28;25(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0431-7. J Biomed Sci. 2018. PMID: 29592806 Free PMC article.
-
Protectin DX suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis through AMPK-HO-1-mediated inhibition of ER stress.Cell Signal. 2017 Jun;34:133-140. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.03.013. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Cell Signal. 2017. PMID: 28342842
-
Beta-Aminoisobutyric Acid as a Novel Regulator of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism.Nutrients. 2019 Feb 28;11(3):524. doi: 10.3390/nu11030524. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30823446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling metabolite β-aminoisobutyric acid as a metabolic regulator, biomarker, and potential exercise pill.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 May 29;14:1192458. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1192458. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37313446 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
β-Aminoisobutyric acid, L-BAIBA, protects PC12 cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via activation of the AMPK and PI3K/Akt pathway.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2021 Dec 7;12:65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2021.12.001. eCollection 2022 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 35024688 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Fermentation of Hyaluronan with Different Molecular Weights by Human Gut Microbiota: Differential Effects on Gut Microbiota Structure and Metabolic Function.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Apr 28;15(9):2103. doi: 10.3390/polym15092103. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37177246 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights of exercise therapy in disease prevention and treatment.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 May 29;9(1):138. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01841-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38806473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-aminoisobutyrics acid, a metabolite of BCAA, activates the AMPK/Nrf-2 pathway to prevent ferroptosis and ameliorates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury.Mol Med. 2023 Dec 4;29(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00729-z. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 38049750 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise-Generated β-Aminoisobutyric Acid (BAIBA) Reduces Cardiomyocyte Metabolic Stress and Apoptosis Caused by Mitochondrial Dysfunction Through the miR-208b/AMPK Pathway.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Feb 25;9:803510. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.803510. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35282369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu J. & Kaufman R. J. From acute ER stress to physiological roles of the Unfolded Protein Response. Cell Death. Differ. 13, 374–384 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

