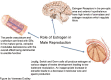
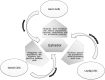
The role of estradiol in male reproductive function
- PMID: 26908066
- PMCID: PMC4854098
- DOI: 10.4103/1008-682X.173932
The role of estradiol in male reproductive function
Abstract
Traditionally, testosterone and estrogen have been considered to be male and female sex hormones, respectively. However, estradiol, the predominant form of estrogen, also plays a critical role in male sexual function. Estradiol in men is essential for modulating libido, erectile function, and spermatogenesis. Estrogen receptors, as well as aromatase, the enzyme that converts testosterone to estrogen, are abundant in brain, penis, and testis, organs important for sexual function. In the brain, estradiol synthesis is increased in areas related to sexual arousal. In addition, in the penis, estrogen receptors are found throughout the corpus cavernosum with high concentration around neurovascular bundles. Low testosterone and elevated estrogen increase the incidence of erectile dysfunction independently of one another. In the testes, spermatogenesis is modulated at every level by estrogen, starting with the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal axis, followed by the Leydig, Sertoli, and germ cells, and finishing with the ductal epithelium, epididymis, and mature sperm. Regulation of testicular cells by estradiol shows both an inhibitory and a stimulatory influence, indicating an intricate symphony of dose-dependent and temporally sensitive modulation. Our goal in this review is to elucidate the overall contribution of estradiol to male sexual function by looking at the hormone's effects on erectile function, spermatogenesis, and libido.
Figures
Comment in
-
Estradiol exerts alterations in sexual function and fertility in human males.Asian J Androl. 2016 May-Jun;18(3):441. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.179157. Asian J Androl. 2016. PMID: 27048785 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Endocrinology of testicular neoplasms.Urology. 1981 Feb;17(2):119-25. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(81)90217-x. Urology. 1981. PMID: 6781115 Review.
-
Effect of high intratesticular estrogen on the seminiferous epithelium in adult male rats.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2005 Sep 28;241(1-2):41-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2005.04.011. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15936871
-
Heterotopic transplantation as a model to study the regulation of spermatogenesis; some histomorphological considerations about sperm decline in man.Contracept Fertil Sex. 1997 Jul-Aug;25(7-8):549-55. Contracept Fertil Sex. 1997. PMID: 9343904
-
Permanent effects of neonatal estrogen exposure in rats on reproductive hormone levels, Sertoli cell number, and the efficiency of spermatogenesis in adulthood.Endocrinology. 1999 Nov;140(11):5364-73. doi: 10.1210/endo.140.11.7108. Endocrinology. 1999. PMID: 10537168
-
Cell-cell interactions in the control of spermatogenesis as studied using Leydig cell destruction and testosterone replacement.Am J Anat. 1990 May;188(1):3-20. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001880103. Am J Anat. 1990. PMID: 2161173 Review.
Cited by
-
Causal associations between COVID-19 and erectile dysfunction: a Mendelian randomization study.J Int Med Res. 2024 Sep;52(9):3000605241274236. doi: 10.1177/03000605241274236. J Int Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39246066 Free PMC article.
-
A short-term high-fat diet alters rat testicular activity and blood-testis barrier integrity through the SIRT1/NRF2/MAPKs signaling pathways.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 27;14:1274035. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1274035. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38027181 Free PMC article.
-
Estradiol, obesity and hypogonadism.Physiol Res. 2020 Sep 30;69(Suppl 2):S273-S278. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934510. Physiol Res. 2020. PMID: 33094625 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between hydration status, male sexual dysfunction and depression in hemodialysis patients.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018 Mar 13;14:523-529. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S147723. eCollection 2018. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018. PMID: 29559788 Free PMC article.
-
NAFLD as a Sexual Dimorphic Disease: Role of Gender and Reproductive Status in the Development and Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Inherent Cardiovascular Risk.Adv Ther. 2017 Jun;34(6):1291-1326. doi: 10.1007/s12325-017-0556-1. Epub 2017 May 19. Adv Ther. 2017. PMID: 28526997 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Travison TG, Morley JE, Araujo AB, O’Donnell AB, McKinlay JB. The relationship between libido and testosterone levels in aging men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:2509–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources