Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Humanized Mice Infected with HIV-1
- PMID: 26908312
- PMCID: PMC4808832
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21522
Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Humanized Mice Infected with HIV-1
Abstract
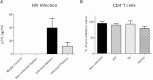
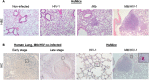
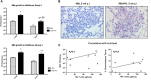
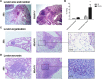
Co-infection with HIV increases the morbidity and mortality associated with tuberculosis due to multiple factors including a poorly understood microbial synergy. We developed a novel small animal model of co-infection in the humanized mouse to investigate how HIV infection disrupts pulmonary containment of Mtb. Following dual infection, HIV-infected cells were localized to sites of Mtb-driven inflammation and mycobacterial replication in the lung. Consistent with disease in human subjects, we observed increased mycobacterial burden, loss of granuloma structure, and increased progression of TB disease, due to HIV co-infection. Importantly, we observed an HIV-dependent pro-inflammatory cytokine signature (IL-1β, IL-6, TNFα, and IL-8), neutrophil accumulation, and greater lung pathology in the Mtb-co-infected lung. These results suggest that in the early stages of acute co-infection in the humanized mouse, infection with HIV exacerbates the pro-inflammatory response to pulmonary Mtb, leading to poorly formed granulomas, more severe lung pathology, and increased mycobacterial burden and dissemination.
Figures
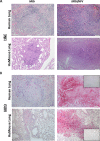

 p < 0.05;
p < 0.05; 
 p < 0.01;
p < 0.01;

 p < 0.001.
p < 0.001.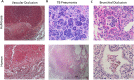
References
-
- Organization, W. H. (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2014).
-
- Khan F. A. et al.. Treatment of active tuberculosis in HIV-coinfected patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis 50, 1288–99 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Law K. F., Jagirdar J., Weiden M. D., Bodkin M. & Rom W. N. Tuberculosis in HIV-positive patients: cellular response and immune activation in the lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 153, 1377–84 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Markowitz N. et al.. Incidence of tuberculosis in the United States among HIV-infected persons. The Pulmonary Complications of HIV Infection Study Group. Ann Intern Med 126, 123–32 (1997). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

