ANXA11 regulates the tumorigenesis, lymph node metastasis and 5-fluorouracil sensitivity of murine hepatocarcinoma Hca-P cells by targeting c-Jun
- PMID: 26908448
- PMCID: PMC4941315
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7484
ANXA11 regulates the tumorigenesis, lymph node metastasis and 5-fluorouracil sensitivity of murine hepatocarcinoma Hca-P cells by targeting c-Jun
Abstract
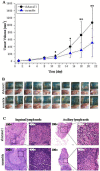
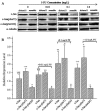
Annexin A11 (Anxa11) is associated with various cancers. Using a pair of syngeneic murine hepatocarcinoma cells, Hca-P with ~25% and Hca-F with ~75% lymph node metastatic (LNM) potentials, we demonstrated Anxa11 involvement in hepatocarcinoma lymphatic metastasis. Here, ANXA11 acted as a suppressor for the tumorigenicity, LNM and 5-FU resistance of Hca-P via c-Jun. We constructed monoclonal Hca-P cell line with stable ANXA11 knockdown. Although Bax and Bcl-2 levels increased in shRNA-Anxa11-transfected Hca-P, ANXA11 downregulation showed no clear effect on Hca-P apoptosis. ANXA11 downregulation promoted in vitro migration and invasion capacities of Hca-P. In situ adhesion potential of Hca-P cells toward LN was significantly enhanced following ANXA11 downregulation. Consistently, ANXA11 downregulation promoted the in vivo tumor growth and LNM capacities of Hca-P cells. ANXA11 knockdown enhanced the chemoresistance of Hca-P cells specifically toward 5-FU instead of cisplatin. Its downregulation increased c-Jun (pSer73) and decreased c-Jun (pSer243) levels in Hca-P. c-Jun (pSer243) downregulation seemed to be only correlated with ANXA11 knockdown without the connection to 5-FU treatment. Interestingly, compared with scramble-Hca-P cells, the levels of c-Jun and c-Jun (pSer73) in shRNA-Anxa11-Hca-P cells were upregulated in the presences of 0.1 and 1.0 mg/L 5-FU. The levels changes from c-Jun and c-Jun (pSer73) in Hca-P cells showed a more obvious tendency with the combination of ANXA11 knockdown and 5-FU treatment. ANXA11 level regulates LNM and 5-FU resistance of Hca-P via c-Jun pathway. It might play an important role in hepatocarcinoma cell malignancy and be a therapeutic target for hepatocarcinoma.
Keywords: Anxa11; c-Jun; chemoresistance; hepatocarcinoma; lymphatic metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Annexin A11 knockdown inhibits in vitro proliferation and enhances survival of Hca-F cell via Akt2/FoxO1 pathway and MMP-9 expression.Biomed Pharmacother. 2015 Mar;70:58-63. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.01.011. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 25776480
-
Anxa5 mediates the in vitro malignant behaviours of murine hepatocarcinoma Hca-F cells with high lymph node metastasis potential preferentially via ERK2/p-ERK2/c-Jun/p-c-Jun(Ser73) and E-cadherin.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:645-654. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.086. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27697636
-
CRKL knockdown promotes in vitro proliferation, migration and invasion, in vivo tumor malignancy and lymph node metastasis of murine hepatocarcinoma Hca-P cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2015 Apr;71:84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.02.022. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 25960220
-
Annexin A11 in disease.Clin Chim Acta. 2014 Apr 20;431:164-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.01.031. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Clin Chim Acta. 2014. PMID: 24508622 Review.
-
Proteomic research progress in lymphatic metastases of cancers.Clin Transl Oncol. 2012 Jan;14(1):21-30. doi: 10.1007/s12094-012-0757-7. Clin Transl Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22262715 Review.
Cited by
-
Annexin Animal Models-From Fundamental Principles to Translational Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 26;22(7):3439. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073439. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33810523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-124-3p Suppresses the Invasiveness and Metastasis of Hepatocarcinoma Cells via Targeting CRKL.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Sep 15;7:223. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00223. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33094104 Free PMC article.
-
Pathobiological functions and clinical implications of annexin dysregulation in human cancers.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 28;10:1009908. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1009908. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36247003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-429 suppresses tumor migration and invasion by targeting CRKL in hepatocellular carcinoma via inhibiting Raf/MEK/ERK pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 5;8(1):2375. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20258-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29403024 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of Annexin A11 (ANXA11) Inhibits Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration via the AKT/GSK-3β Pathway in Gastric Cancer.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Jan 7;24:149-160. doi: 10.12659/msm.905372. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29306955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1118–1127. - PubMed
-
- Shen Q, Bae HJ, Eun JW, Kim HS, Park SJ, Shin WC, Lee EK, Park S, Park WS, Lee JY, Nam SW. MiR-101 functions as a tumor suppressor by directly targeting nemo-like kinase in liver cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014;344:204–211. - PubMed
-
- Tang ZY. Hepatocellular carcinoma surgery-review of the past and prospects for the 21st century. J Surg Oncol. 2005;91:95–96. - PubMed
-
- Lyoo K, Hong SW, Kim SW, Yoon HY, Yoon SK. Silencing of 14-3-3zeta over-expression in hepatocellular carcinoma inhibits tumor growth and enhances chemosensitivity to cis- diammined dichloridoplatium. Cancer Lett. 2011;303:99–107. - PubMed
-
- Hou Z, Ma W, Zhang J, Wang B, Huang Y, Zang S, Tang J, Li L. Enhanced tumorigenesis and lymphatic metastasis of CD133+hepatocarcinoma ascites syngeneic cell lines mediated by JNK signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 2013;67:337–345. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

