Southmedic OxyMask(TM) compared with the Hudson RCI(®) Non-Rebreather Mask(TM): Safety and performance comparison
- PMID: 26909009
- PMCID: PMC4751967
Southmedic OxyMask(TM) compared with the Hudson RCI(®) Non-Rebreather Mask(TM): Safety and performance comparison
Abstract
Background: The non-rebreather mask (NRBM) is used for many applications and in many patient care scenarios in which hypoxemia and resultant hypoxia are a concern. The NRBM is a low-flow oxygen delivery system that is easily deployed and capable of delivering a relatively high fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2).The potential for ineffective carbon dioxide (CO2) removal at low flow rates is a safety concern.
Objective: The authors hypothesized that the use of an OxyMask (Southmedic Inc, Canada) would mitigate these safety concerns while still delivering a relatively high FiO2.
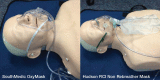
Methods: Bench studies were performed in a third-party laboratory by qualified engineers (Piper Medical, USA). A Harvard Respirator Pump (Harvard Apparatus, USA), oxygen source, CO2 source and a mannequin head were used to simulate varying respiratory conditions. End tidal CO2 (EtCO2), FiO2, fraction of inspired CO2 and percent drop in CO2 in the first second of exhalation were measured at different mask flow rates and respiratory rates. There were two categories of flow rates: high-flow (15 L/min) and low-flow (2 L/min). In each flow group, the above parameters were measured using a tidal volume of 400 mL, inspiratory/expiratory ratio of 1:2, EtCO2 of 5% and a breathing frequency of 15, 20 or 24 breaths/min. Mask performance measurements were obtained and compared.
Conclusion: The OxyMask outperformed the traditional NRBM in each tested category. There was a higher inspired oxygen level, lower inspired CO2 level, and more efficient CO2 clearance at each mask flow level and simulated patient minute volume. This was especially true during conditions in which there were very low mask flow rates.
Historique: Le masque sans réinspiration (MSRI) a de nombreuses applications et sert à de nombreux scénarios de soins aux patients chez qui l’hypoxémie et l’hypoxie qui en découle posent problème. Le MSRI est un système de distribution d’oxygène à faible débit qui est facile à installer et peut insuffler une fraction inspirée d’oxygène (FiO2) relativement élevée. Le potentiel d’élimination inefficace du dioxyde de carbone (CO2) à faible débit représente un problème d’innocuité.
Objectif: Les auteurs ont postulé que l’utilisation d’un OxyMask (SouthMedic Inc, Canada) réduirait ces problèmes d’innocuité tout en insufflant une FiO2 relativement élevée.
Méthodologie: Des ingénieurs diplômés ont effectué des bancs d’essai dans le laboratoire d’un tiers (Piper Medical, États-Unis). Ils ont utilisé une pompe respiratoire Harvard (Harvard Apparatus, États-Unis), une source d’oxygène, une source de CO2 et une tête de mannequin pour simuler diverses conditions respiratoires. Ils ont mesuré le CO2 de fin d’expiration (EtCO2), la FiO2, la fraction inspirée de CO2 et la chute en pourcentage du CO2 pendant la première seconde d’exhalation à divers débits au masque et diverses fréquences respiratoires. Il y avait deux catégories de débit : élevée (15 L/min) et faible (2 L/min). Dans chacun des groupes de débit, les ingénieurs ont mesuré les paramètres précédents au moyen d’un volume courant de 400 mL, d’un ratio entre l’inspiration et l’expiration de 1:2, d’un EtCO2 de 5 % et d’une fréquence respiratoire de 15, 20 ou 24 respirations à la minute. Ils ont obtenu les mesures de rendement des masques et les ont comparées.
Conclusion: L’OxyMask était supérieur au MSRI habituel dans chaque catégorie évaluée. Le taux d’oxygène inspiré était plus élevé, le taux de CO2 inspiré, plus faible, et la clairance de CO2, plus efficace à chaque niveau de débit au masque et chaque ventilation minute simulée des patients, particulièrement lorsque le débit du masque était très faible.
Keywords: Delivery; Hypercarbia; Hypoxemia; Hypoxia; Non-rebreather mask; OxyMask; Oxygen; Respiratory failure.
Figures
References
-
- Abe Y, Kondo T, Yamane Y, et al. The efficacy of an oxygen mask with reservoir bag in patients with respiratory failure. Tokai J Exp Clin Med. 2010;35:144–7. - PubMed
-
- Boumphrey SM, Morris EA, Kinsella SM. 100% inspired oxygen from a Hudson mask-a realistic goal? Resuscitation. 2003;57:69–72. - PubMed
-
- Wagstaff TA, Soni N. Performance of six types of oxygen delivery masks at varying respiratory rates. Anaesthesia. 2007;62:492–503. - PubMed
-
- Wagstaff TAJ. A critical appraisal of ward-based interventions in the care of the acutely unwell patient. Diss Imperial College London. 2011
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources