Antioxidant Systems are Regulated by Nitric Oxide-Mediated Post-translational Modifications (NO-PTMs)
- PMID: 26909095
- PMCID: PMC4754464
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00152
Antioxidant Systems are Regulated by Nitric Oxide-Mediated Post-translational Modifications (NO-PTMs)
Abstract
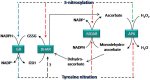
Nitric oxide (NO) is a biological messenger that orchestrates a plethora of plant functions, mainly through post-translational modifications (PTMs) such as S-nitrosylation or tyrosine nitration. In plants, hundreds of proteins have been identified as potential targets of these NO-PTMs under physiological and stress conditions indicating the relevance of NO in plant-signaling mechanisms. Among these NO protein targets, there are different antioxidant enzymes involved in the control of reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as H2O2, which is also a signal molecule. This highlights the close relationship between ROS/NO signaling pathways. The major plant antioxidant enzymes, including catalase, superoxide dismutases (SODs) peroxiredoxins (Prx) and all the enzymatic components of the ascorbate-glutathione (Asa-GSH) cycle, have been shown to be modulated to different degrees by NO-PTMs. This mini-review will update the recent knowledge concerning the interaction of NO with these antioxidant enzymes, with a special focus on the components of the Asa-GSH cycle and their physiological relevance.
Keywords: S-nitrosylation; ascorbate-glutathione cycle; catalase; nitric oxide; peroxiredoxin; superoxide dismutase; tyrosine nitration.
Figures
References
-
- Abello N., Kerstjens H. A. M., Postma D. S., Bischoff R. (2009). Protein tyrosine nitration: selectivity, physicochemical and biological consequences, denitration, and proteomics methods for the identification of tyrosine-nitrated proteins. J. Proteome Res. 8 3222–3238. 10.1021/pr900039c - DOI - PubMed
-
- Asada K. (1992). Ascorbate peroxidase: a hydrogen peroxide-scavenging enzyme in plants. Physiol. Plant. 85 235–241. 10.1111/j.1399-3054.1992.tb04728.x - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

