Identification and Roles of Photosystem II Assembly, Stability, and Repair Factors in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 26909098
- PMCID: PMC4754418
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00168
Identification and Roles of Photosystem II Assembly, Stability, and Repair Factors in Arabidopsis
Abstract
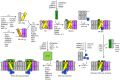
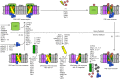
Photosystem II (PSII) is a multi-component pigment-protein complex that is responsible for water splitting, oxygen evolution, and plastoquinone reduction. Components of PSII can be classified into core proteins, low-molecular-mass proteins, extrinsic oxygen-evolving complex (OEC) proteins, and light-harvesting complex II proteins. In addition to these PSII subunits, more than 60 auxiliary proteins, enzymes, or components of thylakoid protein trafficking/targeting systems have been discovered to be directly or indirectly involved in de novo assembly and/or the repair and reassembly cycle of PSII. For example, components of thylakoid-protein-targeting complexes and the chloroplast-vesicle-transport system were found to deliver PSII subunits to thylakoid membranes. Various auxiliary proteins, such as PsbP-like (Psb stands for PSII) and light-harvesting complex-like proteins, atypical short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase family proteins, and tetratricopeptide repeat proteins, were discovered to assist the de novo assembly and stability of PSII and the repair and reassembly cycle of PSII. Furthermore, a series of enzymes were discovered to catalyze important enzymatic steps, such as C-terminal processing of the D1 protein, thiol/disulfide-modulation, peptidylprolyl isomerization, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of PSII core and antenna proteins, and degradation of photodamaged PSII proteins. This review focuses on the current knowledge of the identities and molecular functions of different types of proteins that influence the assembly, stability, and repair of PSII in the higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; Photosystem II assembly; Photosystem II repair; Photosystem II stability; identification and roles.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

