Sharpening coarse-to-fine stereo vision by perceptual learning: asymmetric transfer across the spatial frequency spectrum
- PMID: 26909178
- PMCID: PMC4736933
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.150523
Sharpening coarse-to-fine stereo vision by perceptual learning: asymmetric transfer across the spatial frequency spectrum
Abstract
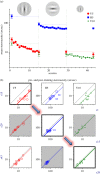
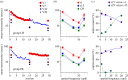
Neurons in the early visual cortex are finely tuned to different low-level visual features, forming a multi-channel system analysing the visual image formed on the retina in a parallel manner. However, little is known about the potential 'cross-talk' among these channels. Here, we systematically investigated whether stereoacuity, over a large range of target spatial frequencies, can be enhanced by perceptual learning. Using narrow-band visual stimuli, we found that practice with coarse (low spatial frequency) targets substantially improves performance, and that the improvement spreads from coarse to fine (high spatial frequency) three-dimensional perception, generalizing broadly across untrained spatial frequencies and orientations. Notably, we observed an asymmetric transfer of learning across the spatial frequency spectrum. The bandwidth of transfer was broader when training was at a high spatial frequency than at a low spatial frequency. Stereoacuity training is most beneficial when trained with fine targets. This broad transfer of stereoacuity learning contrasts with the highly specific learning reported for other basic visual functions. We also revealed strategies to boost learning outcomes 'beyond-the-plateau'. Our investigations contribute to understanding the functional properties of the network subserving stereovision. The ability to generalize may provide a key principle for restoring impaired binocular vision in clinical situations.
Keywords: generalization; specificity; stereopsis; vision enhancement; visual plasticity.
Figures

References
-
- Westheimer G. 1979. The spatial sense of the eye. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 18, 893–912. - PubMed
-
- Roe AW, Parker AJ, Born RT, DeAngelis GC. 2007. Disparity channels in early vision. J. Neurosci. 27, 11 820–11 831. (doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4164-07.2007) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anzai A, DeAngelis GC. 2010. Neural computations underlying depth perception. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 20, 367–375. (doi:10.1016/j.conb.2010.04.006) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nakatsuka C, Zhang B, Watanabe I, Zheng J, Bi H, Ganz L, Smith EL, Harwerth RS, Chino YM. 2007. Effects of perceptual learning on local stereopsis and neuronal responses of V1 and V2 in prism-reared monkeys. J. Neurophysiol. 97, 2612–2626. (doi:10.1152/jn.01001.2006) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chowdhury SA, DeAngelis GC. 2008. Fine discrimination training alters the causal contribution of macaque area MT to depth perception. Neuron 60, 367–377. (doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2008.08.023) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
