A human beta cell line with drug inducible excision of immortalizing transgenes
- PMID: 26909308
- PMCID: PMC4731729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2015.09.008
A human beta cell line with drug inducible excision of immortalizing transgenes
Abstract
Objectives: Access to immortalized human pancreatic beta cell lines that are phenotypically close to genuine adult beta cells, represent a major tool to better understand human beta cell physiology and develop new therapeutics for Diabetes. Here we derived a new conditionally immortalized human beta cell line, EndoC-βH3 in which immortalizing transgene can be efficiently removed by simple addition of tamoxifen.
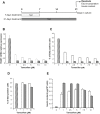
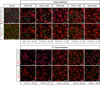
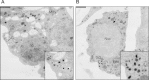
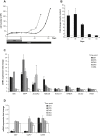
Methods: We used lentiviral mediated gene transfer to stably integrate a tamoxifen inducible form of CRE (CRE-ERT2) into the recently developed conditionally immortalized EndoC βH2 line. The resulting EndoC-βH3 line was characterized before and after tamoxifen treatment for cell proliferation, insulin content and insulin secretion.
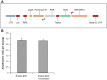
Results: We showed that EndoC-βH3 expressing CRE-ERT2 can be massively amplified in culture. We established an optimized tamoxifen treatment to efficiently excise the immortalizing transgenes resulting in proliferation arrest. In addition, insulin expression raised by 12 fold and insulin content increased by 23 fold reaching 2 μg of insulin per million cells. Such massive increase was accompanied by enhanced insulin secretion upon glucose stimulation. We further observed that tamoxifen treated cells maintained a stable function for 5 weeks in culture.
Conclusions: EndoC βH3 cell line represents a powerful tool that allows, using a simple and efficient procedure, the massive production of functional non-proliferative human beta cells. Such cells are close to genuine human beta cells and maintain a stable phenotype for 5 weeks in culture.
Keywords: Cell engineering; Conditional immortalization; Human beta cell function; Human pancreatic beta cell line; Tamoxifen inducible CRE.
Figures

References
-
- Kroon E., Martinson L.A., Kadoya K., Bang A.G., Kelly O.G., Eliazer S. Pancreatic endoderm derived from human embryonic stem cells generates glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells in vivo. Nature Biotechnology. 2008;26(4):443–452. - PubMed
-
- D'Amour K.A., Bang A.G., Eliazer S., Kelly O.G., Agulnick A.D., Smart N.G. Production of pancreatic hormone-expressing endocrine cells from human embryonic stem cells. Nature Biotechnology. 2006;24(11):1392–1401. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

