Expression data on liver metabolic pathway genes and proteins
- PMID: 26909377
- PMCID: PMC4735467
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2016.01.007
Expression data on liver metabolic pathway genes and proteins
Abstract
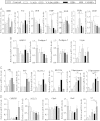
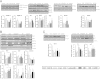
Here, we present the expression data on various metabolic pathways of liver with special emphasize on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism and long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) synthesis, both at gene and protein levels. The data were obtained to understand the effect of vitamin A deficiency on the expression status (both gene and protein levels) of some of the key factors involved in lipogenesis, fatty acid oxidation, triglyceride secretion, long chain PUFA, resolvin D1 synthesis, glucose transport and glycogen synthesis of liver, using modern biology tools, such as quantitative real-time PCR (RT-PCR) and immunoblotting techniques. This data article provides the supporting evidence to the article "Vitamin A deficiency suppresses high fructose-induced triglyceride synthesis and elevates resolvin D1 levels" [1] and therefore, these data may be referred back, for comprehensive understanding and interpretations and for future studies.
Keywords: Glycogen; Lipid; PUFA; Resolvin; Steatosis; Vitamin A.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vitamin A deficiency suppresses high fructose-induced triglyceride synthesis and elevates resolvin D1 levels.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Mar;1861(3):156-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.11.005. Epub 2015 Nov 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26597784
-
The compositional and metabolic responses of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) to a gradient of dietary fish oil and associated n-3 long-chain PUFA content.Br J Nutr. 2017 Dec;118(12):1010-1022. doi: 10.1017/S0007114517002975. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Br J Nutr. 2017. PMID: 29151385
-
Vitamin A and its metabolic pathway play a determinant role in high-fructose-induced triglyceride accumulation of the visceral adipose depot of male Wistar rats.Cell Biochem Funct. 2019 Dec;37(8):578-590. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3434. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Cell Biochem Funct. 2019. PMID: 31495961
-
Nonalcoholic steatosis and steatohepatitis. I. Molecular mechanism for polyunsaturated fatty acid regulation of gene transcription.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001 Oct;281(4):G865-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.2001.281.4.G865. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11557505 Review.
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acid regulation of gene transcription: a molecular mechanism to improve the metabolic syndrome.J Nutr. 2001 Apr;131(4):1129-32. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.4.1129. J Nutr. 2001. PMID: 11285313 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Lactobacillus reuteri Alleviating Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice by Enhancing the Farnesoid X Receptor Signaling Pathway.J Agric Food Chem. 2022 Oct 5;70(39):12550-12564. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c05591. Epub 2022 Sep 26. J Agric Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 36154116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reddy M. Raja Gopal, Kumar C. Pavan, Mahes M., Kumar M. Sravan, Surekha M.V., Kumar P. Uday, Vajreswari A., Jeyakumar S.M. Vitamin A deficiency suppresses high fructose-induced triglyceride synthesis and elevates resolvin D1 levels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016;1861:156–165. - PubMed
-
- Jeyakumar S.M., Prashant A., Rani K.S., Laxmi R., Vani A., Kumar P.U., Vajreswari A. Chronic consumption of trans-fat-rich diet increases hepatic cholesterol levels and impairs muscle insulin sensitivity without leading to hepatic steatosis and hypertriglyceridemia in female Fischer rats. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2011;58:272–280. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

