Statistical approaches and software for clustering islet cell functional heterogeneity
- PMID: 26909740
- PMCID: PMC4878268
- DOI: 10.1080/19382014.2016.1150664
Statistical approaches and software for clustering islet cell functional heterogeneity
Abstract
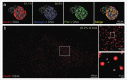
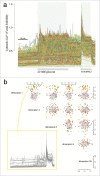
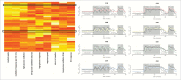
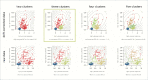
Worldwide efforts are underway to replace or repair lost or dysfunctional pancreatic β-cells to cure diabetes. However, it is unclear what the final product of these efforts should be, as β-cells are thought to be heterogeneous. To enable the analysis of β-cell heterogeneity in an unbiased and quantitative way, we developed model-free and model-based statistical clustering approaches, and created new software called TraceCluster. Using an example data set, we illustrate the utility of these approaches by clustering dynamic intracellular Ca(2+) responses to high glucose in ∼300 simultaneously imaged single islet cells. Using feature extraction from the Ca(2+) traces on this reference data set, we identified 2 distinct populations of cells with β-like responses to glucose. To the best of our knowledge, this report represents the first unbiased cluster-based analysis of human β-cell functional heterogeneity of simultaneous recordings. We hope that the approaches and tools described here will be helpful for those studying heterogeneity in primary islet cells, as well as excitable cells derived from embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent cells.
Keywords: calcium signals; insulin; oscillations.
Figures
References
-
- Johnson JD, Luciani DS. Mechanisms of pancreatic β-cell apoptosis in diabetes and its therapies. Adv Exp Med Biol 2010; 654:447-62; PMID:20217509; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-3271-3_19 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Szabat M, Page MM, Panzhinskiy E, Skovso S, Mojibian M, Fernandez-Tajes J, Bruin JE, Bround MJ, Lee JT, Xu EE, et al.. Reduced insulin production relieves endoplasmic Reticulum stress and induces β cell proliferation. Cell Metab 2015; 23(1):179-93; PMID:26626461 - PubMed
-
- Shapiro AM, Ricordi C, Hering BJ, Auchincloss H, Lindblad R, Robertson RP, Secchi A, Brendel MD, Berney T, Brennan DC, et al.. International trial of the Edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. N Engl J Med 2006; 355:1318-30; PMID:17005949; http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa061267 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Warnock GL, Thompson DM, Meloche RM, Shapiro RJ, Ao Z, Keown P, Johnson JD, Verchere CB, Partovi N, Begg IS, et al.. A multi-year analysis of islet transplantation compared with intensive medical therapy on progression of complications in type 1 diabetes. Transplantation 2008; 86:1762-6; PMID:19104418; http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e318190b052 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rezania A, Bruin JE, Arora P, Rubin A, Batushansky I, Asadi A, O'Dwyer S, Quiskamp N, Mojibian M, Albrecht T, et al.. Reversal of diabetes with insulin-producing cells derived in vitro from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 2014; 32:1121-33; PMID:25211370; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3033 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
