Effects of disturbed blood flow during exercise on endothelial function: a time course analysis
- PMID: 26909789
- PMCID: PMC4792509
- DOI: 10.1590/1414-431X20155100
Effects of disturbed blood flow during exercise on endothelial function: a time course analysis
Abstract
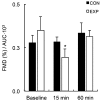
This study aimed to examine the time course of endothelial function after a single handgrip exercise session combined with blood flow restriction in healthy young men. Nine participants (28 ± 5.8 years) completed a single session of bilateral dynamic handgrip exercise (20 min with 60% of the maximum voluntary contraction). To induce blood flow restriction, a cuff was placed 2 cm below the antecubital fossa in the experimental arm. This cuff was inflated to 80 mmHg before initiation of exercise and maintained through the duration of the protocol. The experimental arm and control arm were randomly selected for all subjects. Brachial artery flow-mediated dilation (FMD) and blood flow velocity profiles were assessed using Doppler ultrasonography before initiation of the exercise, and at 15 and 60 min after its cessation. Blood flow velocity profiles were also assessed during exercise. There was a significant increase in FMD 15 min after exercise in the control arm compared with before exercise (64.09% ± 16.59%, P=0.001), but there was no change in the experimental arm (-12.48% ± 12.64%, P=0.252). FMD values at 15 min post-exercise were significantly higher for the control arm in comparison to the experimental arm (P=0.004). FMD returned to near baseline values at 60 min after exercise, with no significant difference between arms (P=0.424). A single handgrip exercise bout provoked an acute increase in FMD 15 min after exercise, returning to near baseline values at 60 min. This response was blunted by the addition of an inflated pneumatic cuff to the exercising arm.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evidence of sex differences in the acute impact of oscillatory shear stress on endothelial function.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019 Feb 1;126(2):314-321. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00729.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 1. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019. PMID: 30382805 Free PMC article.
-
Thirty minutes of handgrip exercise potentiates flow-mediated dilatation in response to sustained and transient shear stress stimuli to a similar extent.Exp Physiol. 2018 Oct;103(10):1326-1337. doi: 10.1113/EP087065. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Exp Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30055018
-
Effects of handgrip training with venous restriction on brachial artery vasodilation.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010 Jul;42(7):1296-302. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181ca7b06. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010. PMID: 20019641 Free PMC article.
-
Shear stress mediates endothelial adaptations to exercise training in humans.Hypertension. 2010 Feb;55(2):312-8. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.146282. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Hypertension. 2010. PMID: 20048193
-
The impact of a cold pressor test on brachial artery handgrip exercise-induced flow-mediated dilation.Vasc Med. 2015 Oct;20(5):409-16. doi: 10.1177/1358863X15586473. Epub 2015 May 28. Vasc Med. 2015. PMID: 26021703
Cited by
-
Potential Implications of Blood Flow Restriction Exercise on Vascular Health: A Brief Review.Sports Med. 2020 Jan;50(1):73-81. doi: 10.1007/s40279-019-01196-5. Sports Med. 2020. PMID: 31559565 Review.
-
Effects of exercise training with blood flow restriction on vascular function in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PeerJ. 2021 Jul 7;9:e11554. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11554. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34277146 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise-mediated adaptations in vascular function and structure: Beneficial effects in coronary artery disease.World J Cardiol. 2021 Sep 26;13(9):399-415. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v13.i9.399. World J Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 34621486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of four weeks blood flow restricted resistance training on macro- and micro-vascular function in healthy, young men.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2023 Oct;123(10):2179-2189. doi: 10.1007/s00421-023-05230-3. Epub 2023 May 28. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37245196 Clinical Trial.
-
Acute effects of physical exercise with different levels of blood flow restriction on vascular reactivity and biomarkers of muscle hypertrophy, endothelial function and oxidative stress in young and elderly subjects - A randomized controlled protocol.Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2021 Mar 25;22:100740. doi: 10.1016/j.conctc.2021.100740. eCollection 2021 Jun. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2021. PMID: 33937579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hambrecht R, Walther C, Mobius-Winkler S, Gielen S, Linke A, Conradi K, et al. Percutaneous coronary angioplasty compared with exercise training in patients with stable coronary artery disease: a randomized trial. Circulation. 2004;109:1371–1378. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000121360.31954.1F. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

