Cost Effectiveness of Free Access to Smoking Cessation Treatment in France Considering the Economic Burden of Smoking-Related Diseases
- PMID: 26909802
- PMCID: PMC4766094
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148750
Cost Effectiveness of Free Access to Smoking Cessation Treatment in France Considering the Economic Burden of Smoking-Related Diseases
Abstract
Context: In France more than 70,000 deaths from diseases related to smoking are recorded each year, and since 2005 prevalence of tobacco has increased. Providing free access to smoking cessation treatment would reduce this burden. The aim of our study was to estimate the incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICER) of providing free access to cessation treatment taking into account the cost offsets associated with the reduction of the three main diseases related to smoking: lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and cardiovascular disease (CVD). To measure the financial impact of such a measure we also conducted a probabilistic budget impact analysis.
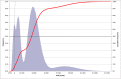
Methods and findings: We performed a cost-effectiveness analysis using a Markov state-transition model that compared free access to cessation treatment to the existing coverage of €50 provided by the French statutory health insurance, taking into account the cost offsets among current French smokers aged 15-75 years. Our results were expressed by the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio in 2009 Euros per life year gained (LYG) at the lifetime horizon. We estimated a base case scenario and carried out a Monte Carlo sensitivity analysis to account for uncertainty. Assuming a participation rate of 7.3%, the ICER value for free access to cessation treatment was €3,868 per LYG in the base case. The variation of parameters provided a range of ICER values from -€736 to €15,715 per LYG. In 99% of cases, the ICER for full coverage was lower than €11,187 per LYG. The probabilistic budget impact analysis showed that the potential cost saving for lung cancer, COPD and CVD ranges from €15 million to €215 million at the five-year horizon for an initial cessation treatment cost of €125 million to €421 million.
Conclusion: The results suggest that providing medical support to smokers in their attempts to quit is very cost-effective and may even result in cost savings.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Rasmussen SR, Prescott E, Sørensen TI, Søgaard J (2004) The total lifetime costs of smoking. The European Journal of Public Health 14: 95–100. - PubMed
-
- WHO (n.d.) REPORT On THE global tobacoo epidemic, 2011. WHO. Available: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789240687813_eng.pdf?ua=1.
-
- Peto R, Lopez AD, Boreham J, Thun M (2006) Mortality from smoking in developed countries 1950–2000 (2nd edition). Available: http://www.ctsu.ox.ac.uk/deathsfromsmoking/download%20files/Original%20r....
-
- OCDE (n.d.) Consomation de tabac- Poucentage de la population de 15+ fumant quotidiennement. Available: http://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/docserver/download/190800142e1t005.pdf?expi.... Accessed 21 May 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

