Peripheral Retinal Vascular Patterns in Patients with Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment in Taiwan
- PMID: 26909812
- PMCID: PMC4766194
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149176
Peripheral Retinal Vascular Patterns in Patients with Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment in Taiwan
Abstract
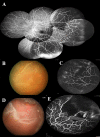
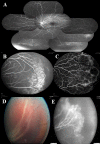
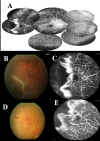
This is an observational study of fluorescein angiography (FA) in consecutive patients with rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD) in Changhua Christian Hospital to investigate the peripheral retinal vascular patterns in those patients. All patients had their age, sex, axial length (AXL), and refraction status (RF) recorded. According to the findings in FA of the peripheral retina, the eyes were divided into 4 groups: in group 1, there was a ramified pattern of peripheral retinal vasculature with gradual tapering; in group 2, there was an abrupt ending of peripheral vasculature with peripheral non-perfusion; in group 3, there was a curving route of peripheral vasculature forming vascular arcades or anastomosis; and in group 4, the same as in group 3, but with one or more wedge-shaped avascular notches. Comparisons of age, sex, AXL, and RF, association of breaks with lattice degeneration and retinal non-perfusion, surgical procedures utilized, and mean numbers of operations were made among the four groups. Of the 73 eyes studied, there were 13 eyes (17.8%) in group 1, 3 eyes (4.1%) in group 2, 40 eyes (54.8%) in group 3 and 17 eyes (23.3%) in group 4. Significant differences in age, AXL and RF, and association of retinal breaks to non-perfusion were noted among the four groups. Patients in group 1 had older ages, while younger ages were noted in groups 3 and 4. Eyes in group 1 had the shortest average AXL and were least myopic in contrast to the eyes in groups 3 and 4. Association of retinal breaks and retinal non-perfusion was significantly higher in groups 2, 3 and 4 than in group 1. In conclusion, peripheral vascular anomalies are common in cases with RRD. Patients with peripheral non-perfusion tend to be younger, with longer axial length and have the breaks associated with retinal non-perfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Rowe JA, Erie JC, Baratz KH, Hodge DO, Gray DT, Butterfield L, et al. Retinal detachment in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1976 through 1995. Ophthalmology 1999;106:154–9. - PubMed
-
- Wong TY, Tielsch JM, Schein OD. Racial difference in the incidence of retinal detachment in Singapore. Arch Ophthalmol 1999;117:379–83. - PubMed
-
- Li X, Beijing Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Study Group. Incidence and epidemiological characteristics of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in Beijing, China. Ophthalmology 2003;110:2413–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

