lncRNA/MicroRNA interactions in the vasculature
- PMID: 26910520
- PMCID: PMC4881297
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.355
lncRNA/MicroRNA interactions in the vasculature
Abstract
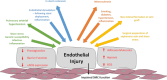
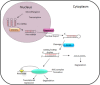
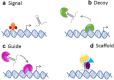
MicroRNA (miRNA) have gained widespread attention for their role in diverse vascular processes including angiogenesis, apoptosis, proliferation, and migration. Despite great understanding of miRNA expression and function, knowledge of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) molecular mechanisms still remains limited. The influence of miRNA on lncRNA function, and the converse, is now beginning to emerge. lncRNA may regulate miRNA function by acting as endogenous sponges to regulate gene expression and miRNA have been shown to bind and regulate lncRNA stability. A detailed understanding of the molecular and cellular effects of lncRNA-miRNA-mediated interactions in vascular pathophysiology could pave the way for new diagnostic markers and therapeutic approaches, but first there is a requirement for a more detailed understanding of the impact of such regulatory networks.
© 2016 The Authors. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Figures


References
-
- West, N.E. et al Nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) gene transfer modifies venous bypass graft remodeling: effects on vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation and superoxide production. Circulation 104(13), 1526–1532 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Buttery, L.D. et al Explanted vein grafts with an intact endothelium demonstrate reduced focal expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase specific to atherosclerotic sites. J. Pathol. 179(2), 197–203 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Libby, P. , Ridker, P.M. & Hansson, G.K. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature 473(7347), 317–325 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

