Plant protein glycosylation
- PMID: 26911286
- PMCID: PMC5045529
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cww023
Plant protein glycosylation
Abstract
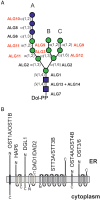
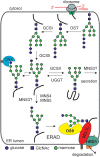
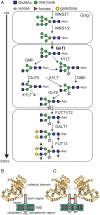
Protein glycosylation is an essential co- and post-translational modification of secretory and membrane proteins in all eukaryotes. The initial steps of N-glycosylation and N-glycan processing are highly conserved between plants, mammals and yeast. In contrast, late N-glycan maturation steps in the Golgi differ significantly in plants giving rise to complex N-glycans with β1,2-linked xylose, core α1,3-linked fucose and Lewis A-type structures. While the essential role of N-glycan modifications on distinct mammalian glycoproteins is already well documented, we have only begun to decipher the biological function of this ubiquitous protein modification in different plant species. In this review, I focus on the biosynthesis and function of different protein N-linked glycans in plants. Special emphasis is given on glycan-mediated quality control processes in the ER and on the biological role of characteristic complex N-glycan structures.
Keywords: Golgi apparatus; N-glycan processing; N-glycosylation; endoplasmic reticulum; glycosyltransferase.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

References
-
- Atmodjo MA, Sakuragi Y, Zhu X, Burrell AJ, Mohanty SS, Atwood JA, Orlando R, Scheller HV, Mohnen D. 2011. Galacturonosyltransferase (GAUT)1 and GAUT7 are the core of a plant cell wall pectin biosynthetic homogalacturonan:galacturonosyltransferase complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:20225–20230. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakker H, Lommen A, Jordi W, Stiekema W, Bosch D. 1999. An Arabidopsis thaliana cDNA complements the N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I deficiency of CHO Lec1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 261:829–832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

