A Distributed Network for Social Cognition Enriched for Oxytocin Receptors
- PMID: 26911697
- PMCID: PMC4764667
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2409-15.2016
A Distributed Network for Social Cognition Enriched for Oxytocin Receptors
Abstract
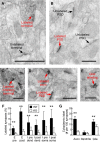
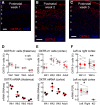
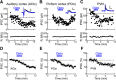
Oxytocin is a neuropeptide important for social behaviors such as maternal care and parent-infant bonding. It is believed that oxytocin receptor signaling in the brain is critical for these behaviors, but it is unknown precisely when and where oxytocin receptors are expressed or which neural circuits are directly sensitive to oxytocin. To overcome this challenge, we generated specific antibodies to the mouse oxytocin receptor and examined receptor expression throughout the brain. We identified a distributed network of female mouse brain regions for maternal behaviors that are especially enriched for oxytocin receptors, including the piriform cortex, the left auditory cortex, and CA2 of the hippocampus. Electron microscopic analysis of the cerebral cortex revealed that oxytocin receptors were mainly expressed at synapses, as well as on axons and glial processes. Functionally, oxytocin transiently reduced synaptic inhibition in multiple brain regions and enabled long-term synaptic plasticity in the auditory cortex. Thus modulation of inhibition may be a general mechanism by which oxytocin can act throughout the brain to regulate parental behaviors and social cognition.
Keywords: antibody; auditory cortex; development; inhibition; oxytocin; synaptic plasticity.
Copyright © 2016 the authors 0270-6474/16/362517-19$15.00/0.
Figures










References
-
- Bartz JA, Zaki J, Bolger N, Ochsner KN. Social effects of oxytocin in humans: context and person matter. Trends Cogn Sci. 2011;15:301–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 NS086750/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS21072/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DC012527/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD015052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD083211/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY013079/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC009836/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- EY13079/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DC009836/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- P30-HD015052-33/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21MH105846/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DC009635/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH019524/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DC009635/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DC009635/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC015388/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS021072/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC012557/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- K18 DC012527/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS021072/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH105846/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
