MRI evaluation prior to Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI): When to acquire and how to interpret
- PMID: 26911969
- PMCID: PMC4805621
- DOI: 10.1007/s13244-016-0470-0
MRI evaluation prior to Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI): When to acquire and how to interpret
Abstract
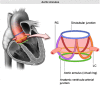
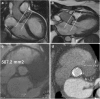
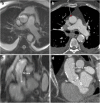
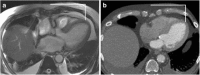
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) is increasingly being used in patients with severe aortic stenosis who are not candidates for surgery. ECG-gated CT angiography (CTA) plays an important role in the preoperative planning for these devices. As the number of patients undergoing these procedures increases, a subset of patients is being recognized who have contraindications to iodinated contrast medium, either due to a prior severe allergic type reaction or poor renal function. Another subgroup of patients with low flow and low gradient aortic stenosis is being recognized that are usually assessed for severity of aortic stenosis by stress echocardiography. There are contraindications to stress echocardiography and some of these patients may not be able to undergo this test. Non-contrast MRI can be a useful emerging modality for evaluating these patients. In this article, we discuss the emerging indications of non-contrast MRI in preoperative assessment for TAVI and describe the commonly used MRI sequences. A comparison of the most important measurements obtained for TAVI assessment on CTA and MRI from same subjects is included. Teaching Points • MRI can be used for preoperative assessment of aortic annulus. • MRI is an alternate to CTA when iodinated contrast is contraindicated. • Measurements obtained by non-contrast MRI are similar to contrast enhanced CTA. • MRI can be used to assess severity of aortic stenosis.
Keywords: Magnetic resonance imaging; Non-contrast MRI; Severe aortic stenosis; Transcatheter aortic valve implantation; Transcatheter aortic valve replacement.
Figures



References
-
- Quail MA, Nordmeyer J, Schievano S, Reinthaler M, Mullen MJ, Taylor AM. Use of cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging for TAVR assessment in patients with bioprosthetic aortic valves: comparison with computed tomography. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81:3912–3917. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.07.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- (2013) ACR Manual on contrast media
-
- Pontone G, Andreini D, Bartorelli AL, et al. Aortic annulus area assessment by multidetector computed tomography for predicting paravalvular regurgitation in patients undergoing balloon-expandable transcatheter aortic valve implantation: a comparison with transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography. Am Heart J. 2012;164:576–584. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2012.06.024. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

