Alternative Polyadenylation of mRNAs: 3'-Untranslated Region Matters in Gene Expression
- PMID: 26912084
- PMCID: PMC4844933
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2016.0035
Alternative Polyadenylation of mRNAs: 3'-Untranslated Region Matters in Gene Expression
Abstract
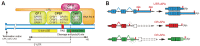
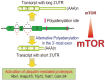
Almost all of eukaryotic mRNAs are subjected to polyadenylation during mRNA processing. Recent discoveries showed that many of these mRNAs contain more than one polyadenylation sites in their 3' untranslated regions (UTR) and that alternative polyadenylation (APA) is prevalent among these genes. Many biological processes such as differentiation, proliferation, and tumorigenesis have been correlated to global APA events in the 3' UTR of mRNAs, suggesting that these APA events are tightly regulated and may play important physiological roles. In this review, recent discoveries in the physiological roles of APA events, as well as the known and proposed mechanisms are summarized. Perspective for future directions is also discussed.
Keywords: 3′ UTR; 3′-end processing; alternative polyadenylation; mTOR; post-transcriptional gene regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reprogramming of 3' untranslated regions of mRNAs by alternative polyadenylation in generation of pluripotent stem cells from different cell types.PLoS One. 2009 Dec 23;4(12):e8419. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008419. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 20037631 Free PMC article.
-
APA-Scan: detection and visualization of 3'-UTR alternative polyadenylation with RNA-seq and 3'-end-seq data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Sep 28;23(Suppl 3):396. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04939-w. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 36171568 Free PMC article.
-
A compendium of conserved cleavage and polyadenylation events in mammalian genes.Genome Res. 2018 Oct;28(10):1427-1441. doi: 10.1101/gr.237826.118. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Genome Res. 2018. PMID: 30143597 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of polyadenylation in health and disease.Nucleus. 2014;5(6):508-19. doi: 10.4161/nucl.36360. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Nucleus. 2014. PMID: 25484187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative polyadenylation of mRNA precursors.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Jan;18(1):18-30. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.116. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 27677860 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of oncomiRs miR-23, miR-24, and miR-27 in the regulation of alternative polyadenylation in glioblastoma via CFIm25 cleavage factor.Metab Brain Dis. 2024 Oct;39(7):1269-1281. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01394-9. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Metab Brain Dis. 2024. PMID: 39190234
-
RNA Binding Protein Rbms1 Enables Neuronal Differentiation and Radial Migration during Neocortical Development by Binding and Stabilizing the RNA Message for Efr3a.Mol Cells. 2022 Aug 31;45(8):588-602. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2022.0044. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Mol Cells. 2022. PMID: 35754370 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CSTF2 in cancer: from technology to clinical application.Cell Cycle. 2023 Dec-Dec;22(23-24):2622-2636. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2299624. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Cell Cycle. 2023. PMID: 38166492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational methods for alternative polyadenylation and splicing in post-transcriptional gene regulation.Exp Mol Med. 2025 Aug;57(8):1631-1640. doi: 10.1038/s12276-025-01496-z. Epub 2025 Aug 14. Exp Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40804481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond Genes: Inclusion of Alternative Splicing and Alternative Polyadenylation to Assess the Genetic Architecture of Predisposition to Voluntary Alcohol Consumption in Brain of the HXB/BXH Recombinant Inbred Rat Panel.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 15;13:821026. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.821026. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35368676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barabino S.M.L., Keller W. Last but not least: fegulated Poly(A) tail formation. Cell. 1999;99:9–11. - PubMed
-
- Bava F., Eliscovich C., Ferreira P.G., Minana B., Ben-Dov C., Guigo R., Valcarcel J., Mendez R. CPEB1 coordinates alternative 3prime]-UTR formation with translational regulation. Nature. 2013;495:121–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

