8-Oxoguanine accumulation in mitochondrial DNA causes mitochondrial dysfunction and impairs neuritogenesis in cultured adult mouse cortical neurons under oxidative conditions
- PMID: 26912170
- PMCID: PMC4766534
- DOI: 10.1038/srep22086
8-Oxoguanine accumulation in mitochondrial DNA causes mitochondrial dysfunction and impairs neuritogenesis in cultured adult mouse cortical neurons under oxidative conditions
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: 8-Oxoguanine accumulation in mitochondrial DNA causes mitochondrial dysfunction and impairs neuritogenesis in cultured adult mouse cortical neurons under oxidative conditions.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 29;6:24696. doi: 10.1038/srep24696. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27128497 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
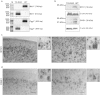
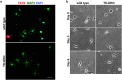
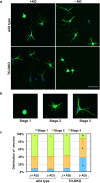
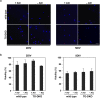
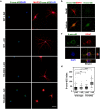
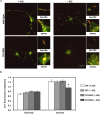
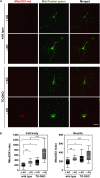
Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction are implicated in aging-related neurodegenerative disorders. 8-Oxoguanine (8-oxoG), a common oxidised base lesion, is often highly accumulated in brains from patients with neurodegenerative disorders. MTH1 hydrolyses 8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine triphosphate (8-oxo-dGTP) to 8-oxo-dGMP and pyrophosphate in nucleotide pools, while OGG1 excises 8-oxoG paired with cytosine in DNA, thereby minimising the accumulation of 8-oxoG in DNA. Mth1/Ogg1-double knockout (TO-DKO) mice are highly susceptible to neurodegeneration under oxidative conditions and show increased accumulation of 8-oxoG in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) in neurons, suggesting that 8-oxoG accumulation in mtDNA causes mitochondrial dysfunction. Here, we evaluated the contribution of MTH1 and OGG1 to the prevention of mitochondrial dysfunction during neuritogenesis in vitro. We isolated cortical neurons from adult wild-type and TO-DKO mice and maintained them with or without antioxidants for 2 to 5 days and then examined neuritogenesis. In the presence of antioxidants, both TO-DKO and wild-type neurons exhibited efficient neurite extension and arborisation. However, in the absence of antioxidants, the accumulation of 8-oxoG in mtDNA of TO-DKO neurons was increased resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction. Cells also exhibited poor neurite outgrowth with decreased complexity of neuritic arborisation, indicating that MTH1 and OGG1 are essential for neuritogenesis under oxidative conditions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MTH1 and OGG1 maintain a low level of 8-oxoguanine in Alzheimer's brain, and prevent the progression of Alzheimer's pathogenesis.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 23;11(1):5819. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84640-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33758207 Free PMC article.
-
8-Oxoguanine causes neurodegeneration during MUTYH-mediated DNA base excision repair.J Clin Invest. 2012 Dec;122(12):4344-61. doi: 10.1172/JCI65053. Epub 2012 Nov 12. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 23143307 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pathophysiology of impaired glucose metabolism, mitochondrial dysfunction, and oxidative DNA damage in Alzheimer's disease brain.Mech Ageing Dev. 2017 Jan;161(Pt A):95-104. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 May 24. Mech Ageing Dev. 2017. PMID: 27233446 Review.
-
MTH1 as a nucleotide pool sanitizing enzyme: Friend or foe?Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Jun;107:151-158. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.002. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 27833032 Review.
-
Oxidative damage in nucleic acids and Parkinson's disease.J Neurosci Res. 2007 Apr;85(5):919-34. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21191. J Neurosci Res. 2007. PMID: 17279544 Review.
Cited by
-
4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal attenuates 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 activity.J Cell Biochem. 2020 Dec;121(12):4887-4897. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29814. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32628320 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial DNA Integrity: Role in Health and Disease.Cells. 2019 Jan 29;8(2):100. doi: 10.3390/cells8020100. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30700008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paricalcitol accelerates BACE1 lysosomal degradation and inhibits calpain-1 dependent neuronal loss in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.EBioMedicine. 2019 Jul;45:393-407. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.07.014. Epub 2019 Jul 11. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31303501 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the molecular mechanism for the differential inhibitory activities of compounds against MTH1.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 11;7:40557. doi: 10.1038/srep40557. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28074893 Free PMC article.
-
Impairment of Glucose Uptake Induced by Elevated Intracellular Ca2+ in Hippocampal Neurons of Malignant Hyperthermia-Susceptible Mice.Cells. 2024 Nov 15;13(22):1888. doi: 10.3390/cells13221888. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39594636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Riemer J. & Kins S. Axonal transport and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurodegener Dis 12, 111–124 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Henchcliffe C. & Beal M. F. Mitochondrial biology and oxidative stress in Parkinson disease pathogenesis. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 4, 600–609 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Kang D., Takeshige K., Sekiguchi M. & Singh K. K. Introduction. In: Mitochondrial DNA mutations in aging, disease and cancer (ed. Singh K. K. ) Ch. 1, 1–15 (Springer-Verlag, 1999).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

