Establishment of age- and sex-adjusted reference data for hand bone mass and investigation of hand bone loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated in clinical practice: an observational study from the DANBIO registry and the Copenhagen Osteoarthritis Study
- PMID: 26912229
- PMCID: PMC4766711
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-0952-y
Establishment of age- and sex-adjusted reference data for hand bone mass and investigation of hand bone loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated in clinical practice: an observational study from the DANBIO registry and the Copenhagen Osteoarthritis Study
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis is characterised by progressive joint destruction and loss of periarticular bone mass. Hand bone loss (HBL) has therefore been proposed as an outcome measure for treatment efficacy. A definition of increased HBL adjusted for age- and sex-related bone loss is lacking. In this study, we aimed to: 1) establish reference values for normal hand bone mass (bone mineral density measured by digital x-ray radiogrammetry (DXR-BMD)); and 2) examine whether HBL is normalised in rheumatoid arthritis patients during treatment with tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors (TNFI).
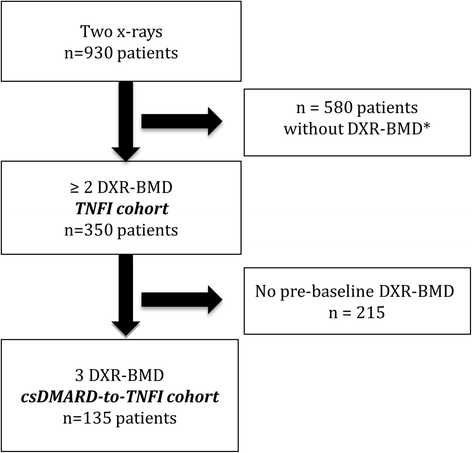
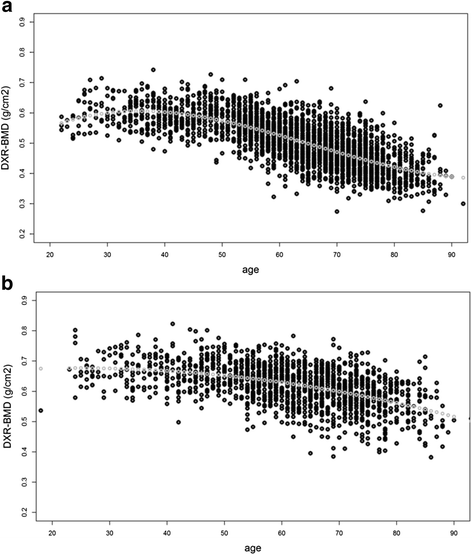
Methods: DXR-BMD was measured from hand x-rays in a reference cohort (1485 men/2541 women) without arthritis randomly selected from an urban Danish population. Sex- and age-related HBL/year was estimated. DXR-BMD was measured in rheumatoid arthritis patients (n = 350: at start of TNFI, and ~2 years after TNFI start), of which 135 patients had three x-rays (~2 years prior to TNFI, at start of TNFI, and ~2 years after TNFI start). Individual HBL/year prior to and during TNFI was calculated and compared to reference values.
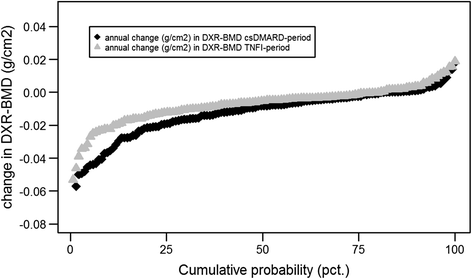
Results: Estimated HBL/year varied strongly with age and sex. Compared to the reference values, 75 % of 135 patients had increased HBL prior to TNFI treatment and 59 % had increased HBL during TNFI treatment (p = 0.17, Chi-squared). In 38 % (38/101) of patients with increased HBL, HBL was normalised during TNFI treatment, whereas 47 % (16/34) of patients with normal HBL prior to TNFI had increased HBL during TNFI treatment. In the 350 patients, increased HBL during TNFI was associated with time-averaged 28-joint disease activity score (odds ratio 1.69 (95 % Confidence Interval 1.34-2.15)/unit increase, p < 0.001), and patients in time-averaged remission had lower HBL than patients without remission (0.0032 vs. 0.0058 g/cm(2)/year; p < 0.001, Mann-Whitney).
Conclusions: We established age- and sex-specific reference values for DXR-BMD in a large cohort without arthritis. HBL was increased in the majority of rheumatoid arthritis patients initiating TNFI in clinical practice, and only normalised in a minority during TNFI.
Figures
References
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987;1988(31):315–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

