Patient-reported quality-of-life analysis of radium-223 dichloride from the phase III ALSYMPCA study
- PMID: 26912557
- PMCID: PMC4843190
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdw065
Patient-reported quality-of-life analysis of radium-223 dichloride from the phase III ALSYMPCA study
Abstract
Background: Radium-223 dichloride (radium-223), a first-in-class α-emitting radiopharmaceutical, is recommended in both pre- and post-docetaxel settings in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and symptomatic bone metastases based on overall survival benefit demonstrated in the phase III ALSYMPCA study. ALSYMPCA included prospective measurements of health-related quality of life (QOL) using two validated instruments: the general EuroQoL 5D (EQ-5D) and the disease-specific Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Prostate (FACT-P).
Patients and methods: Analyses were conducted to determine treatment effects of radium-223 plus standard of care (SOC) versus placebo plus SOC on QOL using FACT-P and EQ-5D. Outcomes assessed were percentage of patients experiencing improvement, percentage of patients experiencing worsening, and mean QOL scores during the study.
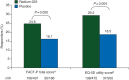
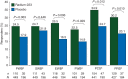
Results: Analyses were carried out on the intent-to-treat population of patients randomized to receive radium-223 (n = 614) or placebo (n = 307). The mean baseline EQ-5D utility and FACT-P total scores were similar between treatment groups. A significantly higher percentage of patients receiving radium-223 experienced meaningful improvement in EQ-5D utility score on treatment versus placebo {29.2% versus 18.5%, respectively; P = 0.004; odds ratio (OR) = 1.82 [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.21-2.74]}. Findings were similar for FACT-P total score [24.6% versus 16.1%, respectively; P = 0.020; OR = 1.70 (95% CI 1.08-2.65)]. A lower percentage of patients receiving radium-223 experienced meaningful worsening versus placebo measured by EQ-5D utility score and FACT-P total score. Prior docetaxel use and current bisphosphonate use did not affect these findings. Treatment was a significant predictor of EQ-5D utility score, with radium-223 associated with higher scores versus placebo (0.56 versus 0.50, respectively; P = 0.002). Findings were similar for FACT-P total score (99.08 versus 95.22, respectively; P = 0.004).
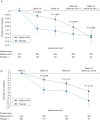
Conclusions: QOL data from ALSYMPCA demonstrated that improved survival with radium-223 is accompanied by significant QOL benefits, including a higher percentage of patients with meaningful QOL improvement and a slower decline in QOL over time in patients with CRPC.
Keywords: castration-resistant prostate cancer; health-related quality of life; patient-reported outcomes; radium-223 dichloride; α-emitter.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Figures
References
-
- Sullivan PW, Mulani PM, Fishman M, Sleep D. Quality of life findings from a multicenter, multinational, observational study of patients with metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Qual Life Res 2007; 16: 571–575. - PubMed
-
- Sullivan PW, Nelson JB, Mulani PM, Sleep D. Quality of life as a potential predictor for morbidity and mortality in patients with metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Qual Life Res 2006; 15: 1297–1306. - PubMed
-
- Weinfurt KP, Li Y, Castel LD et al. . The significance of skeletal-related events for the health-related quality of life of patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Ann Oncol 2005; 16: 579–584. - PubMed
-
- Berruti A, Dogliotti L, Bitossi R et al. . Incidence of skeletal complications in patients with bone metastatic prostate cancer and hormone refractory disease: predictive role of bone resorption and formation markers evaluated at baseline. J Urol 2000; 164: 1248–1253. - PubMed
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Prostate Cancer—v1.2015; http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

