Role of Ih in differentiating the dynamics of the gastric and pyloric neurons in the stomatogastric ganglion of the lobster, Homarus americanus
- PMID: 26912595
- PMCID: PMC4922464
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00737.2015
Role of Ih in differentiating the dynamics of the gastric and pyloric neurons in the stomatogastric ganglion of the lobster, Homarus americanus
Abstract
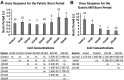
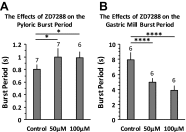
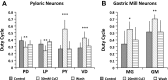
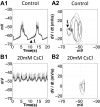
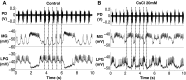
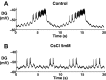
The hyperpolarization-activated inward cationic current (Ih) is known to regulate the rhythmicity, excitability, and synaptic transmission in heart cells and many types of neurons across a variety of species, including some pyloric and gastric mill neurons in the stomatogastric ganglion (STG) in Cancer borealis and Panulirus interruptus However, little is known about the role of Ih in regulating the gastric mill dynamics and its contribution to the dynamical bifurcation of the gastric mill and pyloric networks. We investigated the role of Ih in the rhythmic activity and cellular excitability of both the gastric mill neurons (medial gastric, gastric mill) and pyloric neurons (pyloric dilator, lateral pyloric) in Homarus americanus Through testing the burst period between 5 and 50 mM CsCl, and elimination of postinhibitory rebound and voltage sag, we found that 30 mM CsCl can sufficiently block Ih in both the pyloric and gastric mill neurons. Our results show that Ih maintains the excitability of both the pyloric and gastric mill neurons. However, Ih regulates slow oscillations of the pyloric and gastric mill neurons differently. Specifically, blocking Ih diminishes the difference between the pyloric and gastric mill burst periods by increasing the pyloric burst period and decreasing the gastric mill burst period. Moreover, the phase-plane analysis shows that blocking Ih causes the trajectory of slow oscillations of the gastric mill neurons to change toward the pyloric sinusoidal-like trajectories. In addition to regulating the pyloric rhythm, we found that Ih is also essential for the gastric mill rhythms and differentially regulates these two dynamics.
Keywords: central pattern generator; hyperpolarization-activated inward cationic current.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Dopamine modulation of two subthreshold currents produces phase shifts in activity of an identified motoneuron.J Neurophysiol. 1995 Oct;74(4):1404-20. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.74.4.1404. J Neurophysiol. 1995. PMID: 8989381
-
Central pattern generating neurons simultaneously express fast and slow rhythmic activities in the stomatogastric ganglion.J Neurophysiol. 2006 Jun;95(6):3617-32. doi: 10.1152/jn.00004.2006. Epub 2006 Feb 22. J Neurophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16495367
-
The transient potassium outward current has different roles in modulating the pyloric and gastric mill rhythms in the stomatogastric ganglion.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2017 Apr;203(4):275-290. doi: 10.1007/s00359-017-1162-z. Epub 2017 Mar 18. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28315939
-
Frequency control of a slow oscillatory network by a fast rhythmic input: pyloric to gastric mill interactions in the crab stomatogastric nervous system.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Nov 16;860:226-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb09052.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9928315 Review.
-
Basic principles for generating motor output in the stomatogastric ganglion.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Nov 16;860:35-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb09037.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9928300 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic coupling of signal and preference facilitates sexual isolation during rapid speciation.Proc Biol Sci. 2019 Oct 23;286(1913):20191607. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2019.1607. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Proc Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31640515 Free PMC article.
-
Organelle calcium-derived voltage oscillations in pacemaker neurons drive the motor program for food-seeking behavior in Aplysia.Elife. 2021 Jun 30;10:e68651. doi: 10.7554/eLife.68651. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34190043 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic range of voltage-dependent gap junction signaling is maintained by Ih-induced membrane potential depolarization.J Neurophysiol. 2022 Mar 1;127(3):776-790. doi: 10.1152/jn.00545.2021. Epub 2022 Feb 16. J Neurophysiol. 2022. PMID: 35171723 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of antiphase bursting modulated by the inhibitory synaptic and hyperpolarization-activated cation currents.Front Comput Neurosci. 2024 Feb 9;18:1303925. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2024.1303925. eCollection 2024. Front Comput Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38404510 Free PMC article.
-
Ih Block Reveals Separation of Timescales in Pyloric Rhythm Response to Temperature Changes in Cancer borealis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 6:2024.05.04.592541. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.04.592541. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Oct 15;13:RP98844. doi: 10.7554/eLife.98844. PMID: 38766157 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

