Nanotamoxifen Delivery System: Toxicity Assessment After Oral Administration and Biodistribution Study After Intravenous Delivery of Radiolabeled Nanotamoxifen
- PMID: 26912972
- PMCID: PMC4729022
- DOI: 10.4103/1450-1147.167594
Nanotamoxifen Delivery System: Toxicity Assessment After Oral Administration and Biodistribution Study After Intravenous Delivery of Radiolabeled Nanotamoxifen
Abstract
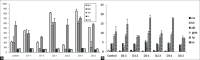
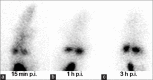
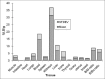
Tamoxifen is the most prescribed anticancer oral drug for increasing overall survival and decreasing recurrence and the risk of contralateral disease. However, some side effects, such as endometrial and liver tumors, thromboembolic disorders, and drug resistance, are associated with long-term tamoxifen treatment. We assessed the hematologic and organ toxicity after oral administration of three different doses of nanotamoxifen formulations. We also performed biodistribution studies of Technetium-99m ((99m)Tc)-nanotamoxifen after intravenous administration. The results demonstrated that nanotamoxifen was well-tolerated, with no adverse effect on biochemical parameters of blood and at the cellular level. Nitric oxide (NO) levels indicated no free radical formation. Oral nanotamoxifen is well-tolerated, with no hepatic or renal toxicity. Intravenous nanotamoxifen has potential to escape the liver, and is known for producing the harmful metabolite 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4OH-tamoxifen), which can cause uterine cancer.
Keywords: Biodistribution; delivery system; free radical formation; nanotamoxifen; oral dose; radiolabeling; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Day R. National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Projet P-1 study (NSABP-1). Quality of life and tamoxifen in a breast cancer prevention trial: A summary of findings from the NSABP P-1 study. National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;949:143–50. - PubMed
-
- Bilimoria MM, Assikis VJ, Jordan VC. Should adjuvant tamoxifen therapy be stopped at 5 years? Cancer J Sci Am. 1996;2:140–50. - PubMed
-
- Frasor J, Stossi F, Danes JM, Komm B, Lyttle CR, Katzenellenbogen BS. Selective estrogen receptor modulators: Discrimination of agonistic versus antagonistic activities by gene expression profiling in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1522–33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

