Genome-wide footprinting: ready for prime time?
- PMID: 26914206
- PMCID: PMC5140282
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.3766
Genome-wide footprinting: ready for prime time?
Abstract
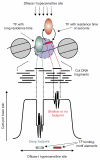
High-throughput sequencing technologies have allowed many gene locus-level molecular biology assays to become genome-wide profiling methods. DNA-cleaving enzymes such as DNase I have been used to probe accessible chromatin. The accessible regions contain functional regulatory sites, including promoters, insulators and enhancers. Deep sequencing of DNase-seq libraries and computational analysis of the cut profiles have been used to infer protein occupancy in the genome at the nucleotide level, a method introduced as 'digital genomic footprinting'. The approach has been proposed as an attractive alternative to the analysis of transcription factors (TFs) by chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq), and in theory it should overcome antibody issues, poor resolution and batch effects. Recent reports point to limitations of the DNase-based genomic footprinting approach and call into question the scope of detectable protein occupancy, especially for TFs with short-lived chromatin binding. The genomics community is grappling with issues concerning the utility of genomic footprinting and is reassessing the proposed approaches in terms of robust deliverables. Here we summarize the consensus as well as different views emerging from recent reports, and we describe the remaining issues and hurdles for genomic footprinting.
Figures
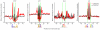


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

