A mixed treatment comparison to compare the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin treatments for cervical dystonia
- PMID: 26914922
- PMCID: PMC4826665
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-016-8050-2
A mixed treatment comparison to compare the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin treatments for cervical dystonia
Abstract
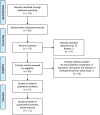
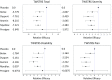
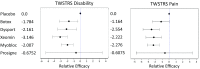
A systematic pair-wise comparison of all available botulinum toxin serotype A and B treatments for cervical dystonia (CD) was conducted, as direct head-to-head clinical trial comparisons are lacking. Five botulinum toxin products: Dysport(®) (abobotulinumtoxinA), Botox(®) (onabotulinumtoxinA), Xeomin(®) (incobotulinumtoxinA), Prosigne(®) (Chinese botulinum toxin serotype A) and Myobloc(®) (rimabotulinumtoxinB) have demonstrated efficacy for managing CD. A pair-wise efficacy and safety comparison was performed for all toxins based on literature-reported clinical outcomes. Multi-armed randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were identified for inclusion using a systematic literature review, and assessed for comparability based on patient population and efficacy outcome measures. The Toronto Western Spasmodic Torticollis Rating Scale (TWSTRS) was selected as the efficacy outcome measurement for assessment. A mixed treatment comparison (MTC) was conducted using a Bayesian hierarchical model allowing indirect comparison of the interventions. Due to the limitation of available clinical data, this study only investigated the main effect of toxin treatments without explicitly considering potential confounding factors such as gender and formulation differences. There was reasonable agreement between the number of unconstrained data points, residual deviance and pair-wise results. This research suggests that all botulinum toxin serotype A and serotype B treatments were effective compared to placebo in treating CD, with the exception of Prosigne. Based on this MTC analysis, there is no significant efficacy difference between Dysport, Botox, Xeomin and Myobloc at week four post injection. Of the adverse events measured, neither dysphagia nor injection site pain was significantly greater in the treatment or placebo groups.
Keywords: Botulinum toxin; Cervical dystonia; Mixed treatment comparison; TWSTRS.
Figures




References
-
- Dashtipour K, Lew M. Cervical dystonia. In: Stacy M, editor. Handbook of dystonia. 2. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2012. pp. 144–158.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

