Plasma Levels and Diagnostic Utility of Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor, Matrix Metalloproteinase-9, and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases-1 as New Biomarkers of Breast Cancer
- PMID: 26915610
- PMCID: PMC4773262
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2016.36.3.223
Plasma Levels and Diagnostic Utility of Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor, Matrix Metalloproteinase-9, and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases-1 as New Biomarkers of Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), and its specific tissue inhibitor - tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) may play an important role in the pathogenesis and spread of cancer. We investigated the plasma levels of M-CSF, MMP-9, and TIMP-1 in comparison with a commonly accepted tumor marker CA 15-3 in breast cancer patients and in control groups.
Methods: The cohort included 110 breast cancer patients in groups at stages I-IV. The control group consisted of 50 healthy volunteers and 50 benign tumor patients. Plasma levels of M-CSF, MMP-9, and TIMP-1 were determined by using ELISA, while CA 15-3 concentrations were determined by using chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA).
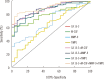
Results: The results showed significant differences in concentrations of the analyzed parameters and in levels of CA 15-3 between the groups of breast cancer patients and the two control groups. Diagnosis using these markers was equal to that using CA 15-3 in terms of sensitivity, predictive values of positive and negativetest results (PPV, NPV) and area under the ROC curve (AUC) in the studied groups. The diagnostic specificities of MMP-9, TIMP-1, M-CSF, and CA 15-3 showed equally high values (95%). The combined use of all tested parameters with CA 15-3 resulted in increased sensitivity, NPV, and AUC, especially in the combination of M-CSF with tumor markers (76%, 64%, and 0.8653).
Conclusions: These findings suggest the tested parameters are useful in the diagnosis of breast cancer patients (except stage I), when combined with CA 15-3.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CA 15-3; M-CSF; MMP-9; TIMP-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma Levels and Diagnostic Utility of M-CSF, MMP-2 and its Inhibitor TIMP-2 in the Diagnostics of Breast Cancer Patients.Clin Lab. 2016 Sep 1;62(9):1661-1669. doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2016.160118. Clin Lab. 2016. PMID: 28164586
-
Plasma levels and diagnostic utility of macrophage-colony stimulating factor, matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 as tumor markers in cervical cancer patients.Tumour Biol. 2018 Jul;40(7):1010428318790363. doi: 10.1177/1010428318790363. Tumour Biol. 2018. PMID: 30052166
-
The pretreatment plasma level and diagnostic utility of M-CSF in benign breast tumor and breast cancer patients.Clin Chim Acta. 2006 Sep;371(1-2):112-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2006.02.033. Epub 2006 Apr 21. Clin Chim Acta. 2006. PMID: 16631152
-
The diagnostic accuracy of macrophage colony-stimulating factor for cervical cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Jul 15;101(28):e29538. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029538. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35839008 Free PMC article.
-
CA 15-3 and related mucins as circulating markers in breast cancer.Ann Clin Biochem. 1999 Sep;36 ( Pt 5):579-86. doi: 10.1177/000456329903600503. Ann Clin Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10505206 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Origin, Polarization, Function, and Reprogramming.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 11;8:607209. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.607209. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33505964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Four Automated Carcinoembryonic Antigen Immunoassays: ADVIA Centaur XP, ARCHITECT I2000sr, Elecsys E170, and Unicel Dxi800.Ann Lab Med. 2018 Jul;38(4):355-361. doi: 10.3343/alm.2018.38.4.355. Ann Lab Med. 2018. PMID: 29611386 Free PMC article.
-
Narrowband ultraviolet B light treatment changes plasma concentrations of MMP-3, MMP-9 and TIMP-3 in psoriatic patients.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017 Apr 27;13:575-582. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S125595. eCollection 2017. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017. PMID: 28490884 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Power of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor in Breast Cancer Patients Based on ROC Analysis.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:5962946. doi: 10.1155/2016/5962946. Epub 2016 Jul 3. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27445439 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Power of Cytokine M-CSF, Metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) and Tissue Inhibitor-2 (TIMP-2) in Cervical Cancer Patients Based on ROC Analysis.Pathol Oncol Res. 2020 Apr;26(2):791-800. doi: 10.1007/s12253-019-00626-z. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 30820752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2014. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2014. p. 4.
-
- Trichopoulos D, Adami HO, Ekbom A, Hsieh CC, Lagiou P. Early life events and conditions and breast cancer risk: from epidemiology to etiology. Int J Cancer. 2008;122:481–485. - PubMed
-
- Harris L, Fritsche H, Mennel R, Norton L, Ravdin P, Taube S, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology 2007 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:5287–5312. - PubMed
-
- Fingleton B. Matrix metalloproteinases: roles in cancer and metastasis. Front Biosci. 2006;11:479–491. - PubMed
-
- Pellikainen JM, Ropponen KM, Kataja VV, Kellokoski JK, Eskelinen MJ, Kosma VM. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in breast cancer with a special reference to activator protein-2, HER2, and prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:7621–7628. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous