Hypoxia as a therapy for mitochondrial disease
- PMID: 26917594
- PMCID: PMC4860742
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aad9642
Hypoxia as a therapy for mitochondrial disease
Abstract
Defects in the mitochondrial respiratory chain (RC) underlie a spectrum of human conditions, ranging from devastating inborn errors of metabolism to aging. We performed a genome-wide Cas9-mediated screen to identify factors that are protective during RC inhibition. Our results highlight the hypoxia response, an endogenous program evolved to adapt to limited oxygen availability. Genetic or small-molecule activation of the hypoxia response is protective against mitochondrial toxicity in cultured cells and zebrafish models. Chronic hypoxia leads to a marked improvement in survival, body weight, body temperature, behavior, neuropathology, and disease biomarkers in a genetic mouse model of Leigh syndrome, the most common pediatric manifestation of mitochondrial disease. Further preclinical studies are required to assess whether hypoxic exposure can be developed into a safe and effective treatment for human diseases associated with mitochondrial dysfunction.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures

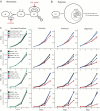
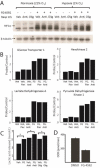
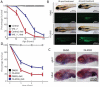


Comment in
-
MITOCHONDRIA. Mitochondrial disease therapy from thin air?Science. 2016 Apr 1;352(6281):31-2. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf5248. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Science. 2016. PMID: 27034357 No abstract available.
-
Applying the Airbrakes: Treating Mitochondrial Disease with Hypoxia.Mol Cell. 2016 Apr 7;62(1):5-6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.03.027. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27058784
References
-
- Rich P. Chemiosmotic coupling: the cost of living. Nature. 2003;421:583. - PubMed
-
- Vafai SB, Mootha VK. Mitochondrial disorders as windows into an ancient organelle. Nature. 2012;491:374–383. - PubMed
-
- Koopman WJ, Willems PH, Smeitink JA. Monogenic mitochondrial disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;366:1132–1141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01DK090311/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 OD017870/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH110049/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HG008171/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 5DP1-MH100706/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- K99-HG008171/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01-MH110049/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 MH100706/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 DK097768/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK097768-03/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090311/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24OD017870/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

