Steak tartare endocarditis
- PMID: 26917729
- PMCID: PMC4769454
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2015-212928
Steak tartare endocarditis
Abstract
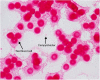
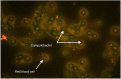
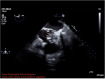
This report describes a case of Campylobacter fetus prosthetic valve infective endocarditis and discusses the subsequent management. Although C. fetus has a tropism for vascular endothelium, infective endocarditis has rarely been reported. In this patient, despite initial optimal antimicrobial therapy, valve replacement was ultimately required due to ongoing infectious emboli to the brain in the setting of evidence of vegetation enlargement on echocardiogram. The prosthetic valve was replaced, the patient completed a 6-week course of parenteral antibiotics after surgical intervention and he made a full recovery with no long-term neurological sequelae. This case highlights the fact that despite the relatively low prevalence of C. fetus endocarditis, it is associated with a high degree of mortality and valve replacement is often indicated.
2016 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
